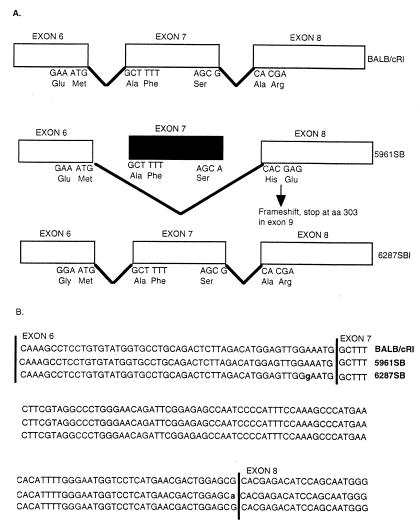
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the murine Fah6287SB and Fah5961SB point mutations and their effect on the processing of the Fah mRNA. (A) Top illustrates the normal splicing pattern for Fah followed by the altered pattern in Fah5961SB and a similar schematic for Fah6287SB. (Middle) As indicated, the Fah5961SB mutation results in an altered pattern of mRNA splicing, causing the loss of exon 7 from the Fah mRNA and a subsequent shift in the reading frame to introduce a premature stop codon in exon 9. Bottom shows the relative position of the missense mutation in Fah6287SB. (B) Nucleotide sequences of Fah exons 6, 7, and 8 of control BALB/cRl (line 1), mutant 6287SB (line 2), and mutant 5961SB (line 3). Mutant Fah6287SB has a point mutation at nucleotide 602, as indicated by the “g” in exon 6 in line 2. Mutant Fah5961SB has a point mutation in the last position of exon 7, as indicated by the “a” in line 3, that destroys the consensus splice donor sequence.