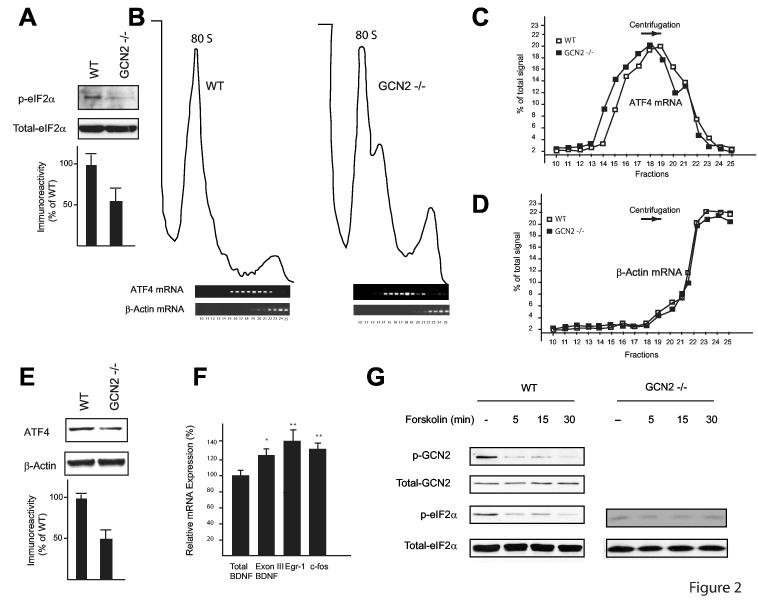
Figure 2.
ATF4 mRNA translation is downregulated in GCN2 -/- mice. A) Western blots performed on hippocampal extracts show that eIF2α phosphorylation is reduced in GCN2 -/- (n=3) as compared to WT mice (n=3). B) In polysome profiles from hippocampal extracts, ATF4 mRNA is in lighter fractions in GCN2 -/- (left panel) than in WT (right panel) controls as determined by RT-PCR analysis. C) Quantification of the band intensities in each fraction from ATF4 mRNA, panel B. D) for data in B, band intensities are quantified for each fraction of β-actin mRNA. E) In pooled hippocampal extracts, expression of ATF4 is reduced in GCN2 -/- mice. F) Real-time RT-PCR analysis reveals increased expression of CREB-dependent genes in hippocampal extracts from GCN2 -/- vs. WT mice (for both, n=5); mRNA expression is given as % of controls; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. G) Forskolin decreases GCN2 and eIF2α phosphorylation. In immunoblots of homogenates of CA1 region (from slices frozen immediately after tetanic stimulation), phosphorylated GCN2 (top) and eIF2α (middle panel) are decreased five minutes after forskolin application.