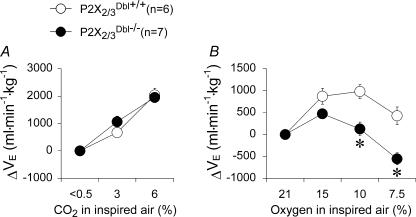
Figure 1. Respiratory responses to hypercapnia and hypoxia in mice with selective deletion of genes encoding P2X2 and P2X3 receptor subunits.
A, changes in ventilation during hypercapnia (3 and 6% CO2 in the inspired air) in conscious P2X2 and P2X3 receptor double knockout (P2X2/3Dbl−/−) and wildtype (P2X2/3Dbl+/+) mice. B, changes in ventilation during hypoxia (15, 10 and 7.5% O2 in the inspired air) in conscious P2X2/3Dbl−/− and P2X2/3Dbl+/+ mice. The resting ventilation during normocapnia/normoxia was identical in the wildtype and knockout animals. The ventilatory response to hypoxia in the P2X3−/− mice was not significantly different from that in P2X3+/+ mice, while in the P2X2−/− mice it was markedly reduced and was similar to that in the P2X2/3Dbl−/−. VE, minute ventilation (respiratory rate × tidal volume). Data are presented as means ± s.e.m. Numbers in parentheses indicate sample sizes. *Significant difference, P < 0.05. Data redrawn with permission from Rong et al. (2003). Copyright 2003 by the Society for Neuroscience.