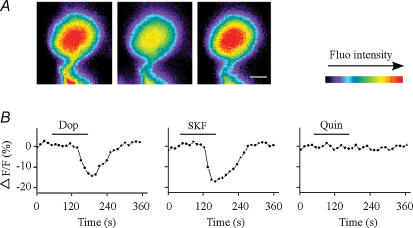
Figure 6. Effect of dopamine or dopamine receptor agonists on Ca2+ influx in isolated RGCs.
A, time lapse images showing cytoplasmic free-Ca2+ concentrations measured before (left), during (middle) and after washout (right) of dopamine. Ca2+ concentrations decreased in response to dopamine treatment, and returned to control levels after washout. Calibration bar, 5 μm. B, cytoplasmic free-Ca2+ concentrations (relative fluorescence intensities) in response to dopamine (Dop), SKF 38393 (SKF; a D1 receptor agonist) or quinpirole (Quin; a D2 receptor agonist) in isolated RGCs. Activation of the D1 but not D2 receptors decreased Ca2+ influx. Horizontal lines indicate the time of drug treatment.