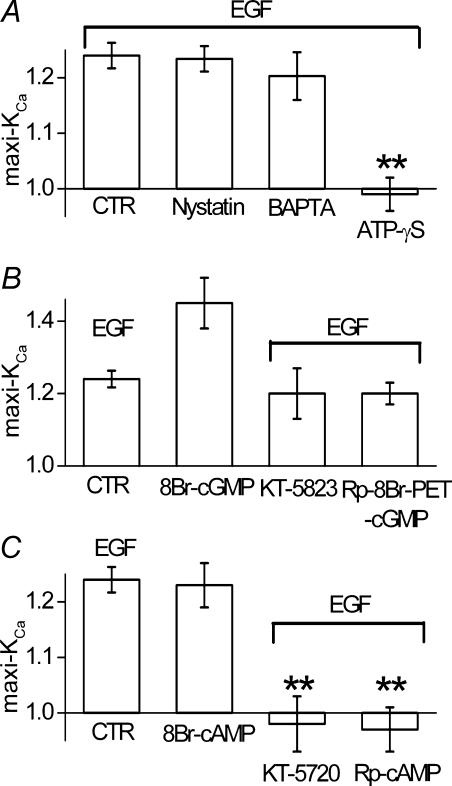
Figure 3. cAK mediates maxi-KCa channel activation by EGFR.
A, bar graph of normalized change in membrane current 8–10 min after addition of EGF (100 ng ml−1), measured using: (i) our ‘standard conditions’, including conventional whole cell technique plus 5 mm EGTA and 5 mm Mg2ATP in the pipette solution (CTR); (ii) a nystatin-perforated patch technique (Nystatin); (iii) our standard conditions except with 10 mm BAPTA instead of EGTA in the pipette (BAPTA); (iv) our standard conditions except with ATP-γS (5 mm) instead of Mg2ATP in the pipette (ATP-γS). B, bar graph of normalized change in membrane current measured using our standard conditions, after addition of EGF (100 ng ml−1) (CTR), after addition of 8-Br-cGMP (100 μm) (8-Br-cGMP), after addition of EGF (100 ng ml−1) in the presence of KT-5823 (1 μm in the bath) (KT-5823), after addition of EGF (100 ng ml−1) in the presence of Rp-8Br-PET-cGMP (1 μm in the pipette) (Rp-8Br-PET-cGMP). C, bar graph of normalized change in membrane current measured using our standard conditions, after addition of EGF (100 ng ml−1) (CTR), after addition of 8-Br-cAMP (100 μm) (8-Br-cAMP), after addition of EGF (100 ng ml−1) in the presence of KT-5720 (1 μm in the bath) (KT-5720), after addition of EGF (100 ng ml−1) in the presence of Rp-cAMP (0.5 μm in the pipette) (Rp-cAMP). **P < 0.01; all measurements of normalized currents were obtained from test pulses to +60 or +80 mV from a holding potential of 0 mV; bars for CTR are from the same data as in Fig. 1C; all bars for data other than CTR represent the mean ± s.e.m. for 5–9 cells.