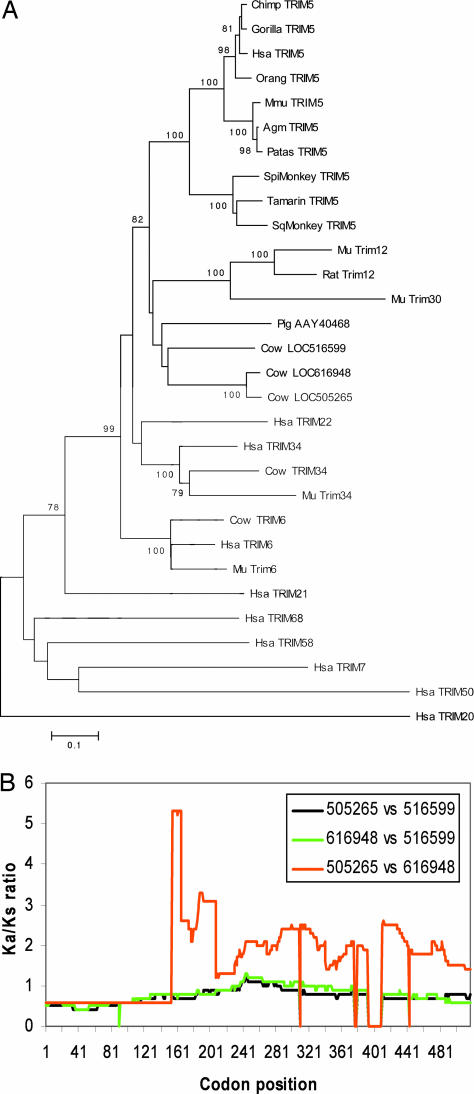
Fig. 1.
Identification of candidate bovine restrictions factors. (A) The predicted amino acid sequences of the proteins encoded by bovine LOC516599, LOC616948, LOC505265, LOC514492 (cow TRIM6) and LOC539820 (cow TRIM34) were aligned with those of other TRIM proteins by using clustal x (50). The alignment was used to build trees in mega3.1 by using neighbor joining, maximum parsimony, the Unweighted Pair Group Method with Authentic Mean (upgma), and maximum evolution methods with 1,000 bootstrap iterations. Values of 100 represent 99–100% concordance in the bootstrap analysis. The scale bar represents evolutionary distance in substitutions/amino acid residue. Hsa, Homo sapiens; Mmu, Macaca mulatta; Spi, spider monkey; Sq, squirrel monkey; Mu, mouse. (B) The plot shows the Ka/Ks ratios at various codon positions for pairwise comparisons of LOC516599, LOC616948, and LOC505265. The alignment is shown in Fig. 5. The Ka/Ks ratio across gaps in the alignment was arbitrarily set to 0. The Ka/Ks ratios, calculated as described (45), were estimated as rolling averages for a window of 200 codons.