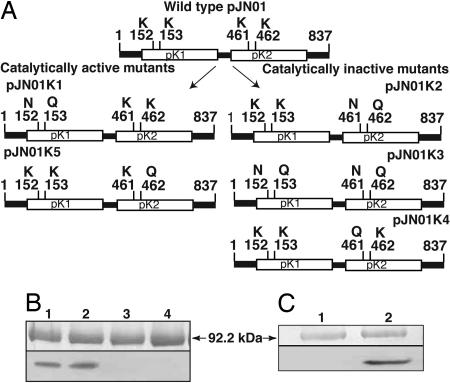
Fig. 4.
Site-directed mutations and their catalytic activity. (A) Lysines 152 and 153 of the pK1 and 461 and 462 of the pK2 domain in the ATP anchor were substituted by asparagine and glutamine separately in each domain and in both domains simultaneously. (B) The pK1 mutant (pJN01K1) retained autophosphorylation activity (lane 2), whereas the pK2 mutant (pJN01K2) and the double mutant (pJN01K3) lost their catalytic activity (lanes 3 and 4). Lysine 461 or 462 was mutated to glutamine in pJN01K4 and pJN01K5, respectively. (C) The pJN01K4 construct lost phosphorylation activity (lane 1), whereas the pJN01K5 retained it (lane 2), identifying lysine 461 as the catalytic residue. Wild-type phosphorylation is presented (B, lane 1), and numbering of the amino acids is according to GenBank (no. AF509747) (9).