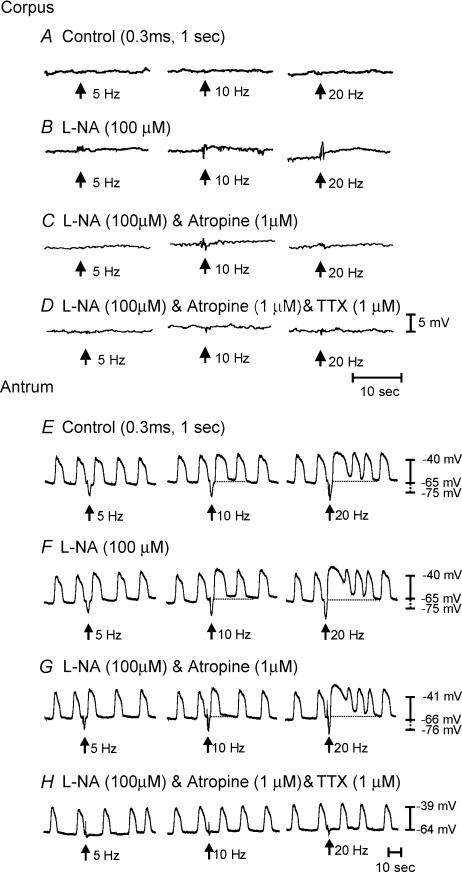
Figure 10. Lack of cholinergic and nitrergic innervation to the longitudinal muscle layer of the corpus and antrum of W/WV mutant animals.
A, lack of response to EFS (0.3 ms, 5–20 Hz for 1 s; arrows) of the corpus under control conditions. B, the lack of effect of l-NA (100 μm). C, EFS evoked little response in the presence of l-NA and atropine (1 μm), and D, TTX (1 μm) also had little effect. E, in the antrum under control conditions, EFS (0.3 ms, 5–20 Hz for 1 s, arrows) produced an IJP that was followed by phase advancement and an increase in the duration of the slow wave immediately following EFS. At higher stimulation frequencies (>10 Hz), there was also a depolarization in membrane potential and an increase in slow-wave frequency for several cycles following EFS. F, l-NA (100 μm) had no effect on the IJP, phase advancement, membrane depolarization and increase in slow-wave frequency immediately following EFS. G, atropine (1 μm) also had no effect on the phase advancement membrane depolarization and increase in slow-wave activity after EFS. However, TTX (1 μm) blocked all nerve-evoked responses except for phase advancement at 20 Hz (H).