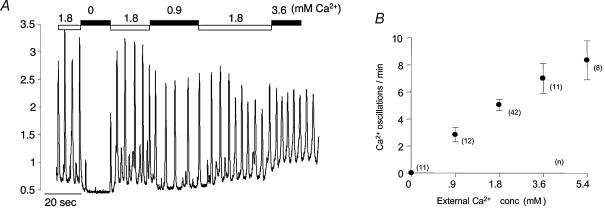
Figure 7. Effect of external Ca2+ concentration.
Reduction of [Ca2+]o from the normal value of 1.8–0 mm (nominally Ca2+-free, since no chelator was present) immediately caused cessation of oscillations and a decrease in basal cytosolic Ca2+. Frequency and amplitude of oscillations were promptly restored on readmission of normal Ca2+. When this solution was changed to one containing 0.9 mm Ca2+, frequency of oscillation was markedly reduced. On the other hand increasing [Ca2+]o to 3.6 mm had the effect of increasing frequency of oscillation. B, the averaged results (numbers of experiments at each concentration are shown alongside each point) (± s.e.m.) at five different Ca2+ concentrations. It can be seen that there is a roughly linear relationship between oscillation frequency and external Ca2+ concentration.