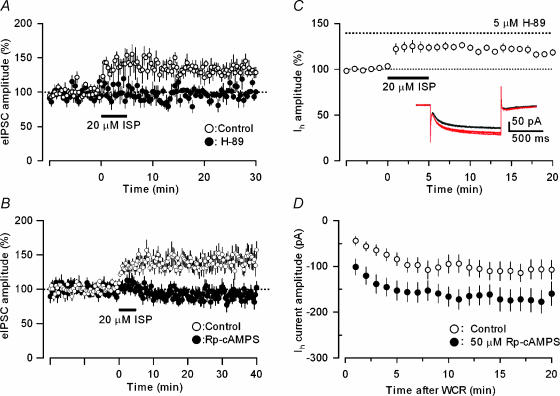
Figure 2. Effects of the PKA inhibitors H-89 and Rp-cAMPS on ISP-induced enhancement of eIPSCs in PCs and hyperpolarization-activated HCN currents in BCs.
A and B, ISP (20 μm), applied during the period indicated by a horizontal bar, increased the eIPSC amplitude in the control solution (○; A, n = 6; B, n = 19), and this effect was abolished by 5 μm H-89 or 100 μm Rp-cAMPS treatment (•; n = 8 and 12 in A and B, respectively). C, ISP increased the amplitude of HCN currents induced by hyperpolarization of BCs from −50 to −100 mV in the presence of the PKA inhibitor H-89 (5 μm, n = 9). D, enhancement of HCN currents of BCs by Rp-cAMPS, a cAMP analogue and PKA inhibitor. Rp-cAMPS (50 μm) was infused into BCs via the recording patch pipette. The graph represents the time course of change in the amplitude of HCN currents induced by a hyperpolarizing voltage step from −50 to −100 mV and recorded with the control internal solution (○, n = 14) and a Rp-cAMPS-containing internal solution (•, n = 18) after the initiation of whole-cell recording (WCR).