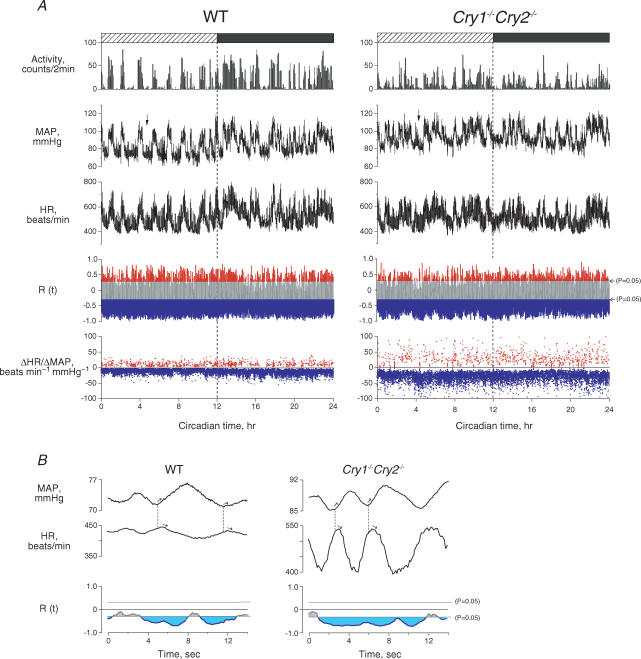
Figure 1. Twenty-four hour profiles of activity, MAP, HR and spontaneous baroreflex sensitivity (ΔHR/ΔMAP) in wild-type (WT) and Cry1−/−Cry2−/− mice.
A, typical example of measurements, from top to bottom: activity, MAP, HR, cross-correlation function (R(t)) between ΔMAP and ΔHR, ΔHR/ΔMAP in a WT (left) and a Cry1−/−Cry2−/− mice (right). R(t) above (red) and below (blue) the lines of P = 0.05 indicate significantly positive and negative correlations, respectively, which were used to determine positive (red) and negative (blue) ΔHR/ΔMAP. B, the areas indicated by arrows in A were enlarged to show dynamic change in MAP and HR. The HR response to a given change in MAP was greater in the Cry1−/−Cry2−/− mouse than in the WT mouse. R(t) in blue indicates a significantly negative correlation at P < 0.05, used to determine spontaneous baroreflex sensitivity (ΔHR/ΔMAP).