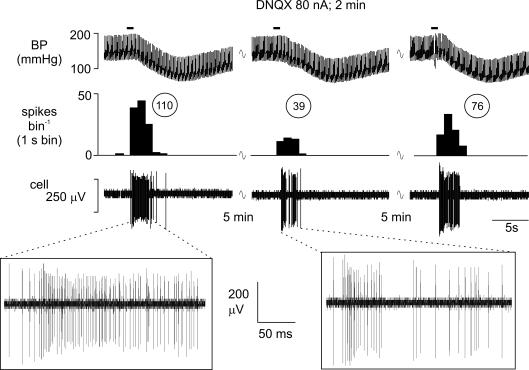
Figure 8. Attenuation of the cardiopulmonary afferent-evoked activation of an NTS neurone by ionophoretically applied DNQX.
Activation of cardiopulmonary afferents by intra-atrial administration of phenylbiguanide (PBG, 12 μg kg−1, 20 μl) at the solid horizontal line evokes a burst of activity (110 spikes) in an NTS neurone (left panel). This excitatory response is reduced to 39 spikes when the same stimulus is given during ionophoretic application of the selective non-NMDA receptor antagonist DNQX (80 nA; middle panel) and recovers to 76 spikes 5 min after removal of the DNQX (right panel). From the top, traces show arterial blood pressure (BP; mmHg), a continuous rate histogram of neuronal activity (spikes bin−1) and the raw recording of neuronal activity (cell, μV).