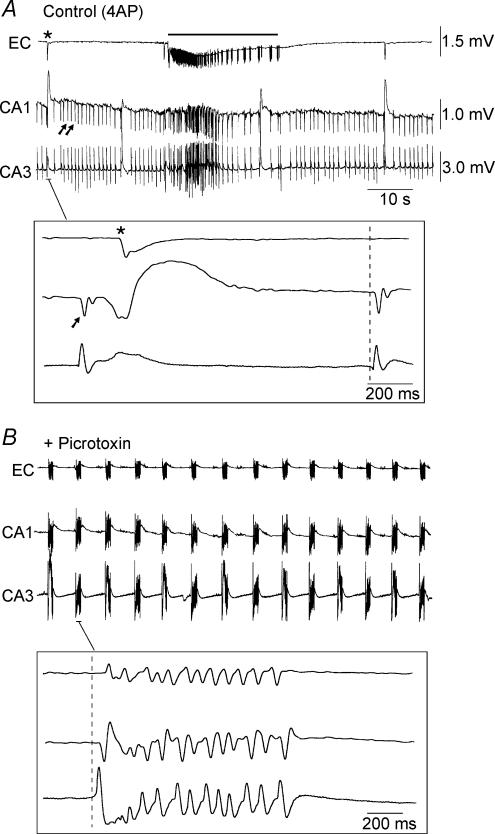
Figure 1. Effect of picrotoxin on 4AP-induced activity in a combined hippocampus–EC slice.
A, simultaneous field potential recordings obtained from EC, CA1 and CA3 during bath application of 4AP. Note that fast interictal discharges (arrows in the CA1 trace) are restricted to the hippocampus (CA3 and CA1) but that slow interictal events (asterisk in the EC trace) are recorded in both hippocampus and EC. Note also the long-lasting ictal discharge (bar). B, picrotoxin application causes loss of ictal discharge in the EC and the appearance of robust interictal discharges that initiate in CA3 and propagate sequentially to CA1 and EC (inset). The insets in A and B show selected interictal events at faster time bases and the dashed lines demonstrate that these discharges initiate in CA3.