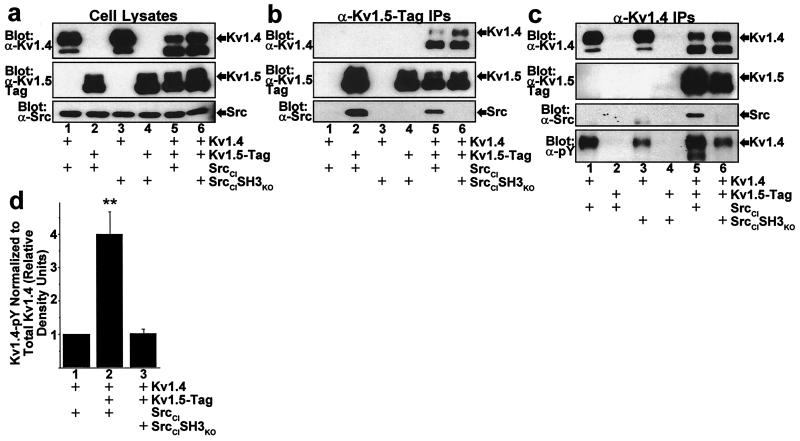
Figure 2.
Stable SH3-dependent association of Src with Kv1.4/Kv1.5 heteromultimeric potassium channels and consequent increased Kv1.4 phosphorylation. (a) Expression of Kv1.4/Kv1.5 heteromultimeric channels with Src PTK in HEK 293 cells. Combinations of Kv1.4, C-peptide epitope-tagged Kv1.5 (Kv1.5-Tag), catalytically impaired Src (SrcCI), and SrcCI with a point mutation in the SH3 domain that abolishes SH3 domain binding to its ligand (SrcCISH3KO) were transfected into HEK 293 cells, followed by Western blot of detergent solubilized cell lysates probed with α−Kv1.4 (Top, n = 6), α−Kv1.5-Tag (Middle, n = 6), or α−Src (Bottom, n = 6) mAbs. The fully processed plasma membrane-targeted forms of Kv1.4 (≈95 kDa) and Kv1.5 (≈80–85 kDa) are indicated by the arrows labeled “Kv1.4” and “Kv1.5,” respectively, and migrate slower than incompletely processed and targeted forms. (b) SrcCI coimmunoprecipitates with Kv1.5 homomultimers and Kv1.4/Kv1.5 heteromultimers, whereas SrcCISH3KO fails to coimmunoprecipitate with either Kv1.5 homomultimers or Kv1.4/Kv1.5 heteromultimers. Cell lysates analyzed in a were immunoprecipitated with α−Kv1.5-Tag mAb and analyzed by Western blot. (c) Stable Src association and increased phosphorylation of Kv1.4 subunits occurs only in Kv1.4/Kv1.5 heteromultimers and depends on Src SH3 domain interaction with the Kv1.5 proline-rich region. Cell lysates analyzed in a were immunoprecipitated with α−Kv1.4 mAb and analyzed by Western blot. SrcCI only coimmunoprecipitates with Kv1.4 when Kv1.4 is coassembled with Kv1.5 in Kv1.4/Kv1.5 heteromultimers. SrcCISH3KO fails to coimmunoprecipitate with Kv1.4, even when Kv1.4 is coassembled in Kv1.4/Kv1.5 heteromultimers. Phosphorylation of fully processed Kv1.4 subunits is increased when coassembled in Kv1.4/Kv1.5 heteromultimers, and this increase is abolished when SrcCI is replaced with SrcCISH3KO. (d) Quantitative comparison of Kv1.4 subunit phosphorylation in cells transfected with combinations of Kv1.4, Kv1.5-Tag, SrcCI, and SrcCISH3KO. Signal density of Kv1.4 phosphorylation detected with α−pY mAb is normalized to the corresponding signal density of Kv1.4 protein detected with α−Kv1.4 mAb. Bars represent relative Kv1.4 normalized phosphotyrosine density for each transfection condition determined within each experiment by dividing the normalized phosphotyrosine density for the indicated transfection condition by the normalized phosphotyrosine density for the Kv1.4/SrcCI transfection condition (mean ± SEM, n = 6; **, P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA).