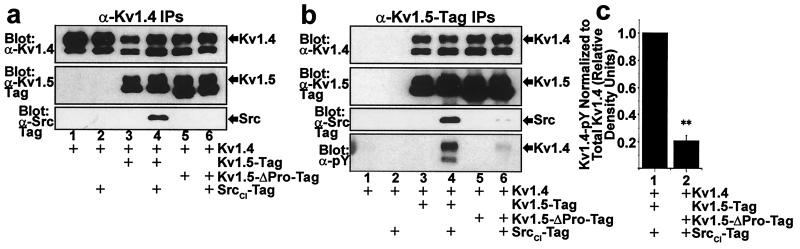
Figure 3.
Increased phosphorylation of Kv1.4 subunits in Kv1.4/Kv1.5 heteromultimers mediated by the interaction of Src with the Kv1.5 proline-rich SH3 domain ligand sequence. (a) Stable association of Src PTK with Kv1.4/Kv1.5 heteromultimeric channels depends on the interaction of Src with the proline-rich 2xRPLPPLP sequence of Kv1.5. Combinations of Kv1.4, Kv1.5-Tag, Kv1.5-ΔPro-Tag, and c-Myc epitope-tagged catalytically impaired Src (SrcCI-Tag) were transfected into HEK 293 cells, followed by Western blot of α−Kv1.4 immunoprecipitates of cell lysates. SrcCI coimmunoprecipitates with Kv1.4/Kv1.5 heteromultimers, but fails to coimmunoprecipitate with either Kv1.4 homomultimers or Kv1.4/Kv1.5-ΔPro heteromultimers. (b) Increased phosphorylation of Kv1.4 subunits by Src in Kv1.4/Kv1.5 heteromultimers depends on the Kv1.5 2xRPLPPLP Src SH3 domain ligand. Cell lysates from a were immunoprecipitated with α−Kv1.5-Tag mAb and analyzed by Western blot. The Kv1.4 subunits coassembled with Kv1.5 exhibit greater tyrosine phosphorylation than the Kv1.4 subunits coassembled with Kv1.5-ΔPro. (c) Quantitative comparison of Kv1.4 subunit phosphorylation in cells transfected with combinations of Kv1.4, Kv1.5-Tag, Kv1.5-ΔPro-Tag, and SrcCI-Tag. Kv1.4 phosphorylation was quantitatively analyzed as in Fig. 2d, but with relative density defined in relation to the normalized density observed for the Kv1.4/Kv1.5-Tag/SrcCI-Tag transfection condition (mean ± SEM, n = 4; **, P < 0.001 by paired t test).