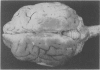
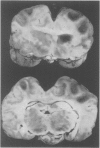
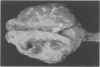
Full text
PDF


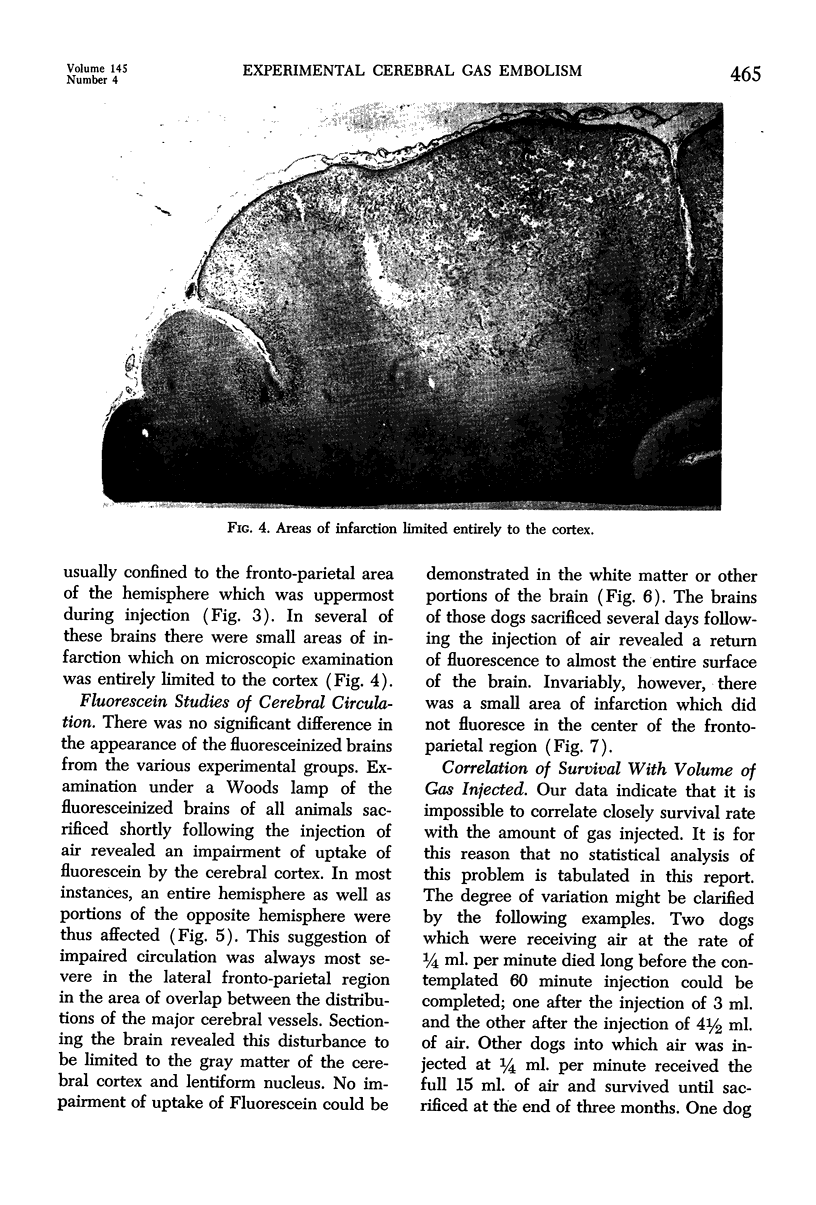
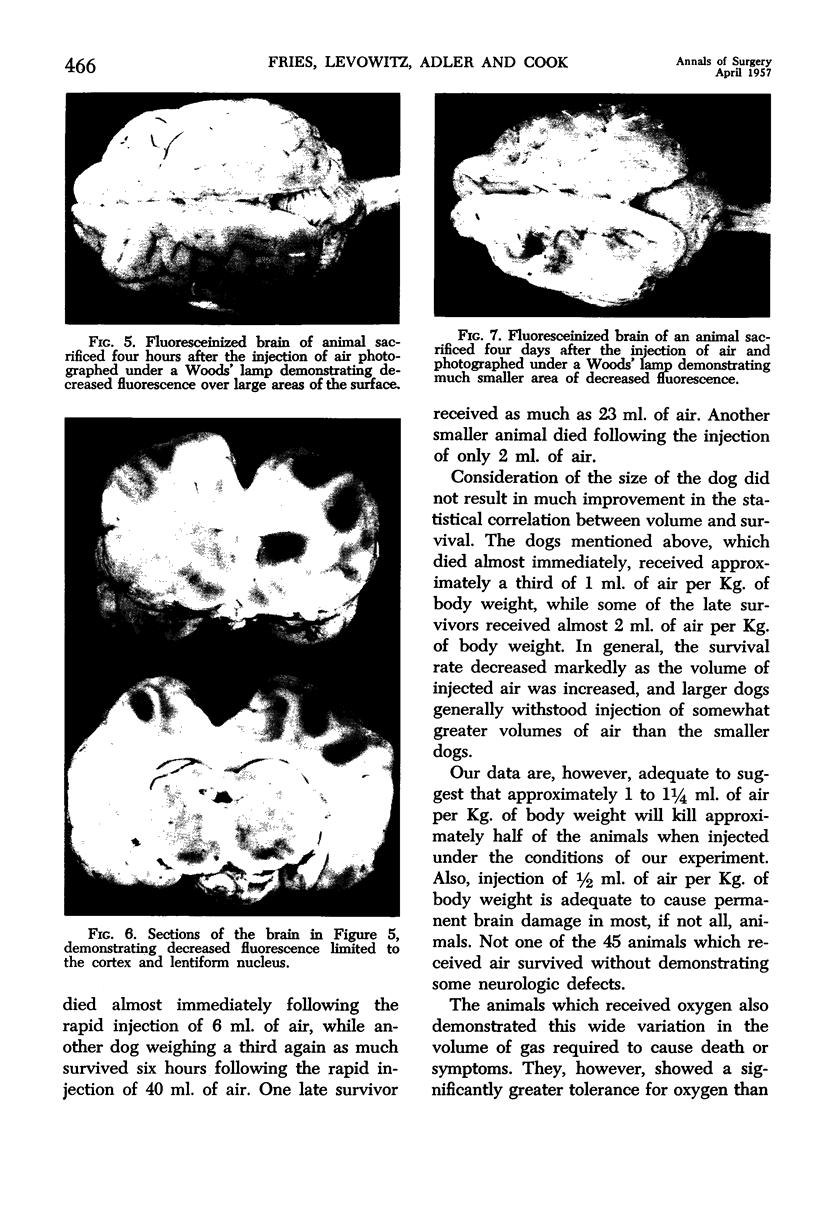




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COLE F. Intravenous oxygen. Anesthesiology. 1951 Mar;12(2):181–188. doi: 10.1097/00000542-195103000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAZIO C., SACCHI U. Experimentally produced red softening of the brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1954 Jul;13(3):476–481. doi: 10.1093/jnen/13.3.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H. F., Coles B. C., Hall G. E. Experimental Gas Embolism: I. Intravenous Air Embolism. Can Med Assoc J. 1937 Jun;36(6):584–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWANK R. L., HAIN R. F. The effect of different sized emboli on the vascular system and parenchyma of the brain. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1952 Jul;11(3):280–299. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195207000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEDRAL J. W., IVY A. C. The relation of circulatory rate to aeroembolism and aeroemphysema. J Aviat Med. 1951 Feb;22(1):13–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]