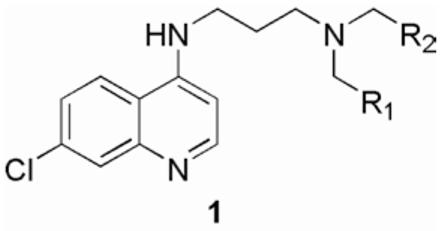
SYNOPSIS TOC Due to growing problems with drug resistance, there is an outstanding need for new, cost-effective drugs for the treatment of malaria. The 4-aminoquinolines have provided a number of useful antimalarials and Plasmodium falciparum, the causative organism for the most deadly form of human malaria, is generally slow to develop resistance to these drugs. Therefore, diverse screening libraries of quinolines continue to be useful for antimalarial drug discovery. We report herein the development of an efficient method for the production of libraries of 4-aminoquinolines variant in the substitutions of the sidechain portion of the molecule and the results of screening this library for activity against P. falciparum.
