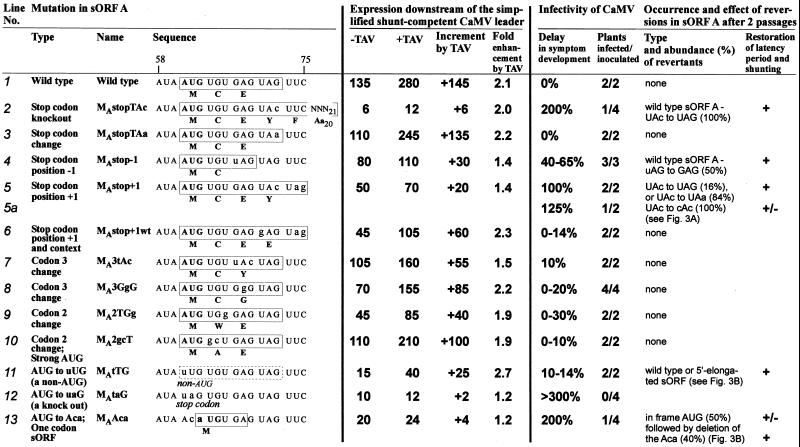
Figure 2.
Correlation between the efficiency of the sORF A-mediated ribosome shunt and infectivity of CaMV. Types, names, and sequences of the sORF A point mutations are shown. Mutated nucleotides are in lowercase. sORF variants are boxed; amino acid sequences indicated below. Expression levels of a CAT reporter ORF placed downstream of the simplified, shunt-competent and TAV-responsive CaMV leader (described in ref. 15 and Methods) are given relative to the nontransactivated expression downstream of the wild-type CaMV leader set to 100% (Fig. 1A). With the simplified leader, a contribution of scanning-dependent expression because of mutations in sORF A could be almost completely excluded (15). Consequently, most of the mutations resulted in a slightly less pronounced negative effect in the context of the wild-type leader (Fig. 3, and other results not shown). Infectivity of the CaMV mutants was studied in turnip plants as described previously (11); delays in symptom development after the first inoculation with viral DNA are given in percent with respect to the time required for symptom appearance with the wild-type virus (i.e., 20 days = 100%). All of the viable mutants developed symptoms visually indistinguishable from the wild-type symptoms characteristic of strain Ca540 (see Methods) even after long delays and reversions.