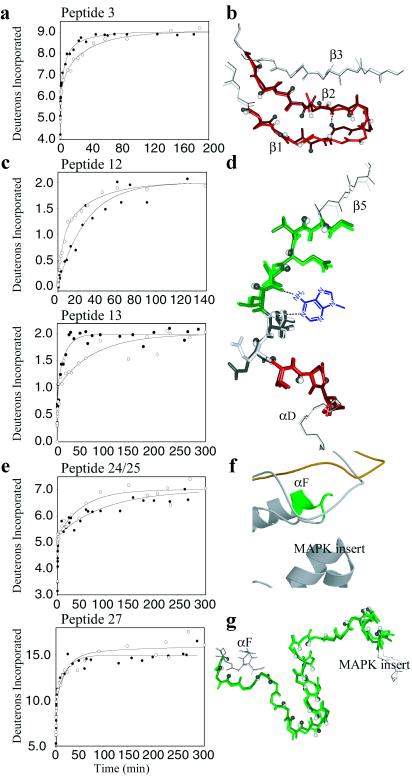
Figure 3.
Comparison of HX/MS data and x-ray structure in the ATP binding loop, hinge, and the extended peptide substrate binding groove. (a) Peptide 3 in the ATP binding loop has 11 amides of which nine exchange, where the increased exchange in ppERK indicates conversion of one slow amide to an intermediate amide (k3(ERK) = 0.024 min-1; k2(ppERK) = 0.16 min-1). (b) Conformational change in peptide 3 for ERK (white, red) and ppERK (gray, dark red), representing amide hydrogens by spheres and the backbone hydrogen bond formed between residues 32 and 35 in ppERK as a dotted line. (c) The hinge peptides 12 and 13 each showed two of four amides exchanging. In peptide 12, the decreased rate is consistent with conversion of one intermediate amide to a slow amide (k2(ERK) = 0.21 min-1; k3(ppERK) = 0.035 min-1), whereas in peptide 13 one slow amide increased in rate (k3(ERK) = 0.013 min-1; k3(ppERK) = 0.060 min-1). Decreased exchange in overlapping peptide 12/ME (not shown) was identical to the decreased exchange in peptide 12, indicating that no change in rate occurred at residues Met-106 and Glu-107, within peptides 12/ME and 13. (d) Superposition of the hinge (rmsdbackbone = 0.33 Å) as in b, showing peptide 12 in green and peptide 13 (excluding Met-106 and Glu-107) in red. Shown in blue is the adenine ring of ATP, which if present would directly contact peptide 12 (28). (e) Peptides 24 and 27 in the extended substrate binding groove. Peptide 24 shows seven of 10 amides exchanging, best fit to decreased rates for both the fast amides (five amides; k1(ERK) = 11 min-1; k1(ppERK) = 3.3 min-1) and the slow amides (two amides; k3(ERK) = 0.019 min-1; k3(ppERK) = 0.010 min-1). Peptide 27 shows 17 of 25 amides exchanging, fit to the conversion of one slow amide (0.002 min-1) to nonexchanging. (f) Ribbon diagram of the substrate binding groove, indicating peptide 24 in green (format as in Fig. 2d). (g) Superposition of peptide 27 of ERK (green) and ppERK (dark green) with rmsdbackbone = 0.50 Å (format as in b).