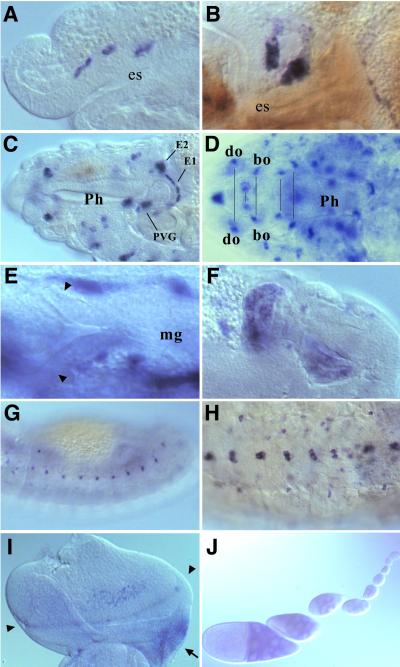
Figure 4.
D-ret expression during organogenesis. In situ hybridization was performed as in Fig. 3. (A) Stage 12. Three invaginations of the stomatogastric nervous system (SNS) anlage express D-ret. (B) Stage 13. SNS cells settling on the foregut. (C) Mature SNS ganglia at stage 16, showing the persistent D-ret expression. EG1 and EG2, first and second esophageal ganglia; PVG, proventricular ganglion (ref. 31). The frontal ganglion of SNS (out of focus) also expresses D-ret. (D) Expression in the cephalopharyngeal ganglia, which appear as paired structures in the head (pairs marked by a line). do, dorsal organ; bo, Bolwig's organ. For the names of the other D-ret-expressing ganglia, see ref. 35. (E) The proctodeum region of a stage 12 embryo. The early malpighian tubule diverticula (arrowheads) do not express D-ret. Pictured signals are the yolk sac expression (see Fig. 3C). (F) Malpighian tubule anlagen transiently show strong D-ret expression at stage 13. Two of the four growing tubules are shown. (G) D-ret expression in the lateral epidermis at stage 13. (H) Ventral neuroectoderm (CNS) expresses D-ret. Stage 16. (I) Eye-antennal imaginal disk of a third-instar larva. D-ret is expressed weakly in the retinal cluster near the morphogenetic furrow (arrowheads). The ocellar region of the presumptive head (arrow) shows strong expression. (J) D-ret expression in germ-line nurse cells in the ovarian follicles, which begins in approximately the fourth follicle from the germarium and gradually increases. However, we were unable to detect D-ret mRNA in the mature oocyte in the egg chamber (not shown) or in the deposited egg at the precellularization stage (Fig. 3A). C and F are composite pictures of two focal planes each. A–C and E–G, lateral views; D, dorsal view; H, ventral view. I, posterior up, medial right.