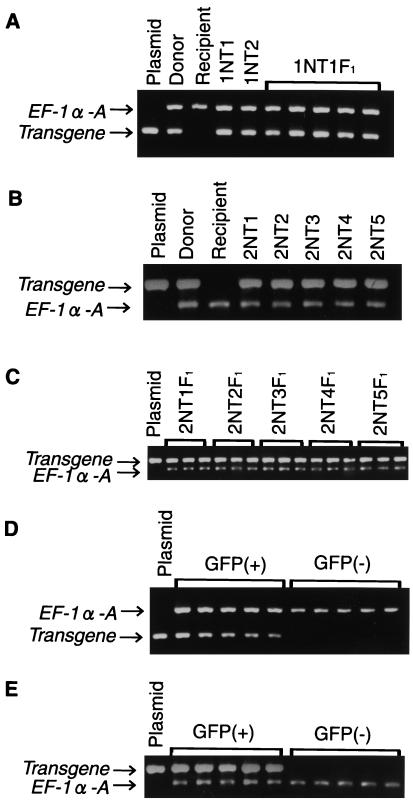
Figure 3.
Detection of the transgene in nuclear transplants and their offspring. (A) EF-1a-A/GFP in nuclear transplants and F1 offspring. Plasmid, pEF-1a-A/GFP; donor, donor transgenic fish; recipient, OR; 1NT1 and 1NT2, nuclear transplants; 1NT1F1, five F1 offspring derived from 1NT1. (B) β-Act/GFP-N in nuclear transplants. Plasmid, pβ-Act/GFP-N; donor, donor transgenic fish; recipient, OR; 2NT1 through 2NT5, nuclear transplants. (C) β-Act/GFP-N in F1 offspring. Plasmid, pβ-Act/GFP-N; 2NT1F1 through 2NT5F1, three each of F1 offspring obtained by crossing 2NT1, 2NT2, 2NT3, 2NT4, and 2NT5 with OR. (D) EF-1a-A/GFP in F2 offspring derived from 1NT1. Plasmid, pEF-1a-A/GFP; GFP (+) and GFP (−), five each F2 offspring exhibiting fluorescence and no fluorescence, respectively. (E) β-Act/GFP-N in F2 offspring derived from 2NT1; plasmid, pβ-Act/GFP-N; GFP (+) and GFP (−), five each F2 offspring exhibiting fluorescence and no fluorescence, respectively. The endogenous EF-1a-A gene is amplified and used as a control in all PCR analyses.