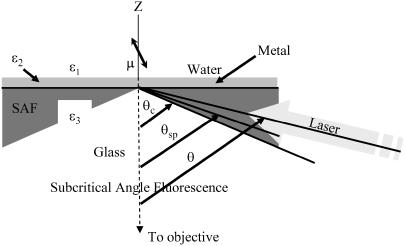
FIGURE 2.
The water/metal/glass multilayer used with TIRM. A dipolar probe (μ) is excited by the evanescent field in the water medium produced by the totally internally reflecting laser beam incident at angle θ. Fluorescence emission from dipole μ propagates in the glass medium in the super- and subcritical angle fluorescence regions and is collected by the objective. SAF originates from the dipole near-field, whereas subcritical angle fluorescence is from the dipole far-field emission. Critical angle θc is the incidence angle beyond which TIR occurs at a glass/water interface with dielectric constants ɛ3 and ɛ1. The SPR angle, θsp, is the incidence angle for peak transmission through the metal film with dielectric constant ɛ2.