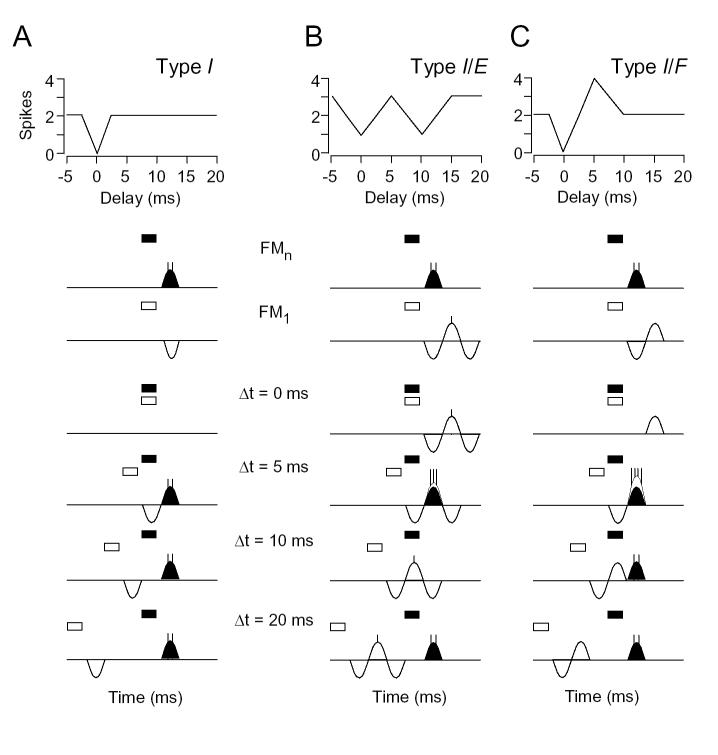
Fig. 10.
Comparison of delay sensitivity for type I (A) and I/E (B) inhibitory combination-sensitive neurons and type I/F (C) facilitatory combination-sensitive neurons. Top: delay curves showing response as function of delay of BF signal after low frequency signal. Bottom: Responses to sounds are represented as inhibitory influences (below baseline), excitatory influences (above baseline), and spikes. These influences may originate below the IC and are thus not necessarily inhibitory and excitatory postsynaptic potentials in IC neurons. The temporal features of inhibition, excitation and facilitation create different delay sensitivity functions.