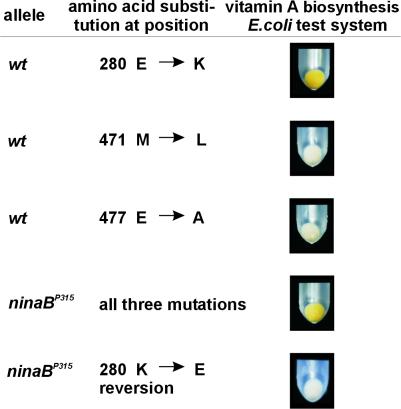
Figure 4.
A single Glu-to-Lys substitution leads to the loss of the β-diox enzymatic activity. The three different mutations found in the β-diox cDNA encoded by the ninaBP315 allele were introduced separately in the wild-type cDNA by site-directed mutagenesis, and the resultant plasmids were tested for enzymatic activity in the E. coli test system. Only the mutation at position 838 leading to a Glu-to-Lys exchange in the deduced amino acid sequence results in a loss of β-diox enzymatic activity, whereas the mutations at positions 1,411 and 1,430 do not affect the enzymatic activity of β-diox. By converting the mutation at position 838 in the ninaBP315 cDNA, the enzymatic activity of the encoded protein could be restored.