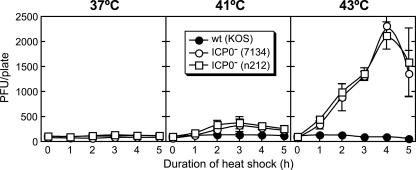
FIG. 2.
The plating efficiencies of ICP0− viruses are enhanced when cells are heat shocked prior to infection. Twenty-four-hour-old Vero cell monolayers in 35-mm plates were incubated for 1 to 5 h at 37°C, 41°C, or 43°C, and at hourly intervals following heat stress, replicate monolayers were infected with ∼100 PFU/plate wild-type (KOS) or ICP0− (7134 or n212) virus. The average number of plaques/plate is shown, and error bars indicate the standard deviations of four independent experiments.