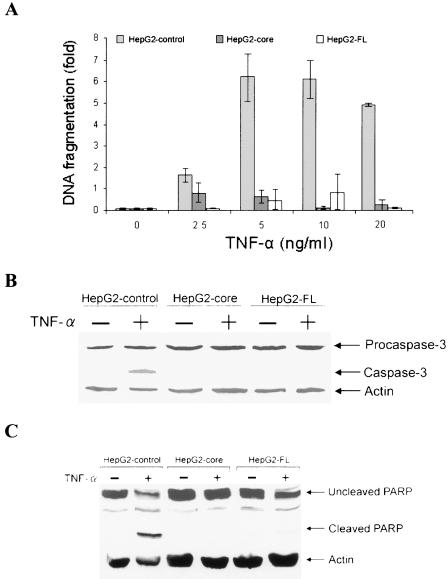
FIG. 1.
HCV core protein inhibits TNF-α-mediated apoptosis in HepG2 cells. (A) Comparison of the fold differences of DNA fragmentation as an index of apoptotic cell death in TNF-α-treated empty vector-transfected HepG2 cells (control) and cells stably transfected with core or FL cDNA of HCV. Cells (5 × 104) were treated with indicated concentrations of TNF-α for 48 h, and cellular DNA fragmentation was measured by a cell death ELISA (Roche). A similar level of DNA fragmentation was observed between 5 to 20 ng of TNF-α/ml. (B) Western blot analysis for the expression status of caspase-3 in control HepG2 cells treated with TNF-α (20 ng/ml) and cells stably transfected with core or FL cDNA for 48 h. The ∼17-kDa band (right) indicates the active form of caspase 3. The level of cellular actin was used as an internal control for comparison of protein load. (C) Similar Western blot analysis for PARP cleavage, as described in the legend to panel B. An ∼85-kDa signature peptide (right) indicates the cleavage product from PARP. The molecular weights of the protein bands were ascertained from the migration of standard protein molecular weight markers (Invitrogen).