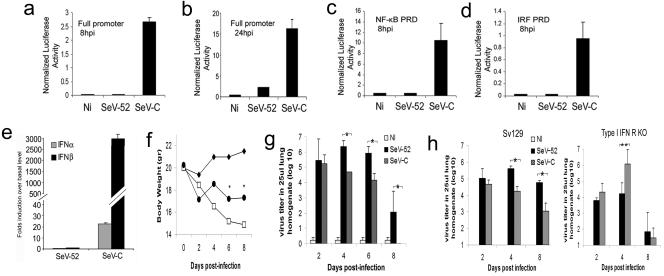
FIG. 1.
Reduced virulence of SeV-C compared to SeV-52 in mice. (a to d) Luciferase activity of whole-cell lysates from NIH 3T3 cells cotransfected with a plasmid constitutively expressing Renilla luciferase and a plasmid containing firefly luciferase reporter constructs driven by either the complete IFN-β promoter (a and b), four copies of the NF-κB PRD of the IFNβ promoter (c), or three copies of the IRF3/7 PRD of the IFN-β promoter (d) and infected with SeV for 8 h (a, c, and d) or 24 h (b). p.i., postinfection. (e) Quantification of IFN-α and -β gene transcripts by quantitative real-time PCR analysis from lung tissue of C57BL/6 mice 6 h after intranasal infection with the same ID50 of SeV-52 or SeV-C. (f) Weight loss of C57BL/6 mice treated with PBS (⧫) or infected with 20 ID50 of SeV-C (•) or SeV-52 (□) (n = 5). An asterisk indicates statistical difference, with a P value of ≤0.05. (g) Virus titer in the lungs of C57BL/6 mice treated with PBS or infected with 20 ID50 of SeV-C or SeV-52. An asterisk indicates statistical difference, with a P value of ≤0.05. (h) Virus titer in the lungs of wild-type Sv129 and type I IFN receptor-deficient (KO) mice infected intranasally with the same ID50 of SeV-52 or SeV-C. Results are representative of more than three independent experiments. An asterisk indicates statistical difference, with a P value of <0.005. The double asterisk indicates a P value of 0.07. Error bars indicate standard deviations.