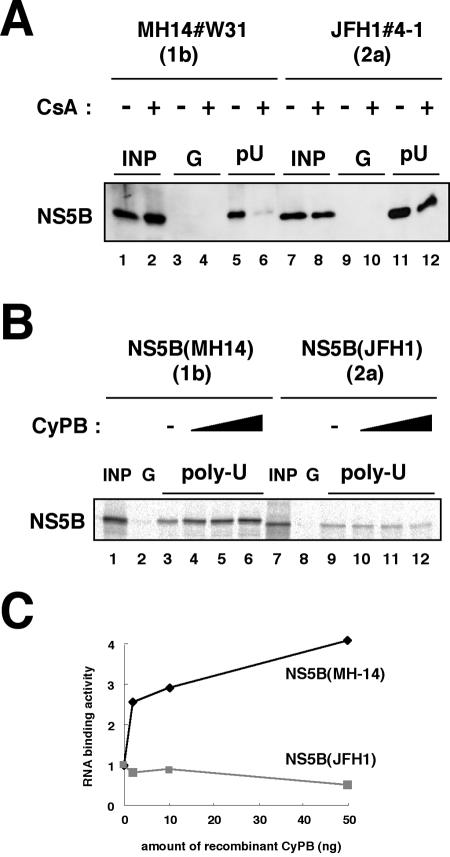
FIG. 7.
RNA binding capacity of JFH1 NS5B was independent of CyPB. (A) An RNA-protein binding precipitation assay was performed using MH14#W31 (NN/1b/SG) cells (lanes 1 to 6) and JFH1#4-1 (JFH1/2a/SG) cells (lanes 7 to 12) as described in Materials and Methods. MH14#W31 (NN/1b/SG) and JFH1#4-1 (JFH1/2a/SG) cells preincubated without (lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11) or with (lanes 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12) CsA were treated with digitonin, followed by digestion with proteinase K to isolate the replication complex. This fraction was then incubated with poly(U) RNA-Sepharose (lanes 5, 6, 11, and 12) or protein G-Sepharose as a negative control (lanes 3, 4, 9, and 10). Precipitates were detected by immunoblot analysis with anti-NS5B antibody. INP, one-sixth of the amount of cell lysate used in the precipitation assay; G and pU, samples with protein G-Sepharose and poly(U)-Sepharose, respectively. (B) An in vitro RNA binding assay was performed as described in Materials and Methods. In vitro-synthesized NS5B of MH-14 (lanes 1 to 6) or JFH1 (lanes 7 to 12) with the rabbit reticulocyte lysate in the presence of [35S]methionine was incubated with protein G-Sepharose (lanes 2 and 8) or poly(U)-Sepharose in the absence (lanes 3 and 9) or presence of various amounts of purified recombinant GST-CyPB (2 ng in panels 4 and 10, 10 ng in panels 5 and 11, and 50 ng in panels 6 and 12). The resultant precipitates were fractionated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, followed by the detection of radiolabeled protein. (C) The density of the bands of NS5B in the RNA binding fraction was quantified and plotted against the amount of the recombinant GST-CyPB (in nanograms). Solid line, NS5B of MH-14; faint line, NS5B of JFH1.