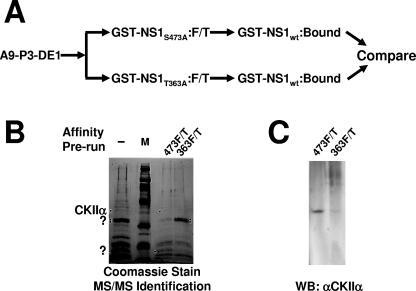
FIG. 2.
Isolation and identification of cellular proteins interacting with wild-type but not nontoxic mutant NS1. (A) Purification of cytotoxicity-related NS1 partner proteins by sequential NS1 affinity chromatography. The P3-DE1 prepurified protein fractions were run first over a column carrying either cytotoxicity mutant of NS1 (T363A or S473A). Unbound proteins (flow-through; F/T) failing to interact with the nontoxic NS1 derivative were then run over a second affinity column coupled with wild-type GST-NS1 to capture cytotoxicity-dependent NS1 partners. After extensive washing, eluates were collected, containing the cellular proteins which bind to wild-type but not cytotoxic mutant NS1 proteins. (B) SDS-PAGE separation and Coomassie blue staining of proteins retained by GST-NS1wt affinity columns and subsequently eluted at 700 mM NaCl. A9 cell proteins from the P3-DE1 fraction (see Fig. 1B) were run over the GST-NS1wt column without prior additional purification (−, total NS1-binding protein) or after prior elimination of proteins binding to either mutant NS1 affinity column (473F/T; proteins lacking affinity to GST-NS1:S473A and binding to wild-type NS1; 363F/T, proteins lacking affinity to GST-NS1:T363A and binding to wild-type NS1). NS1wt partner proteins overrepresented in 474F/T versus 363F/T, and conversely, are marked with dots. Marked bands were cut from the gel and submitted to MS/MS analyses. The 40-kDa species overrepresented in 473F/T (i.e., with a reduced affinity for NS1:S473A) was identified as CKIIα. M, molecular weight markers (Amersham-Pharmacia). (C) This identification was confirmed by Western blotting (WB) of the two protein fractions obtained after differential affinity chromatography with NS1 variants using antibodies specific for CKIIα.