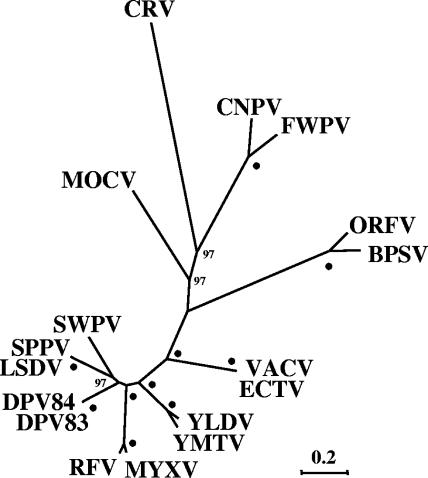
FIG. 5.
Phylogenetic analysis of CRV proteins. Eighty-three conserved proteins between CRV036 and CRV147 were concatenated and aligned with similar data sets from other ChPVs using MUSCLE. The unrooted tree for 32,633 aligned characters was generated using maximum likelihood with WAG correction for multiple substitutions, four-category discrete gamma model, estimation for invariant residues, and 100 bootstrap replicates as implemented in Phyml. Bootstrap values greater than 70 are indicated at appropriate nodes, and dots indicate values of 100. Homologous protein sequences from the following viruses and accession numbers were compared: bovine papular stomatitis virus (BPSV; GenBank accession number AY386265); canarypox virus (CNPV; AY318871); ectromelia virus (ECTV; AF012825); deerpox virus W-848-83 (DPV83; AY689436); deerpox virus W-1170-84 (DPV84; AY689437); fowlpox virus (FWPV; AF198100); lumpy skin disease virus (LSDV; AF325528); molluscum contagiosum virus (MOCV; U60315); myxoma virus (MYXV; AF170726); orf virus (ORFV; AY386264); rabbit (Shope) fibroma virus (SFV; AF170722); sheeppox virus (SPPV; AY077833); swinepox virus (SWPV; AF410153); VACV, M35027; Yaba-like disease virus (YLDV; AJ293568); Yaba monkey tumor virus (YMTV; AY386371). Scale indicates estimated changes per residue. Similar topologies were obtained using an alignment (22,055 characters) in which poorly aligned regions were trimmed with Gblocks; using additional maximum likelihood analyses of the MUSCLE alignment as implemented in PHYLIP, TREE-PUZZLE, IQPNNI, and MRBAYES; using similar analyses on alignments generated with with Dialign-T and Kalign; using Phyml results for supertree analysis of multiple concatenated datasets and for supertree analysis of individual proteins aligned with Kalign; or by conducting similar analyses on a data set including only one virus per genus or major viral group (10 taxa).