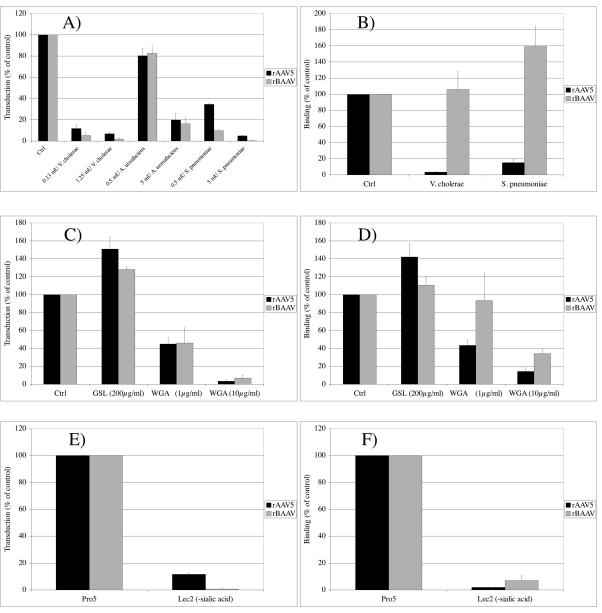
FIG. 1.
BAAV transduction and cell attachment are sialic acid dependent. The effects of enzymatic removal of terminal cell surface sialic acid groups from COS cells on transduction with rAAV5-GFP and rBAAV-GFP (A) and binding (B) were studied by pretreatment of the cells with neuraminidases from A. ureafaciens, V. cholerae, or S. pneumoniae. The dependence of rBAAV transduction and cell attachment on terminal and nonterminal sialic acid groups was studied by lectin competition assays (C and D) with the sialic acid-specific lectin WGA and by comparing transduction (E) and binding (F) of recombinant virus to the sialic acid-deficient CHO mutant Lec2 or the parental Pro5 cells. Virus binding was determined by quantitative PCR after 1 h of transduction at 4°C. Transduction efficiency was analyzed 24 hours after transduction by flow cytometry. The values are means from three experiments; the error bars represent standard deviations.