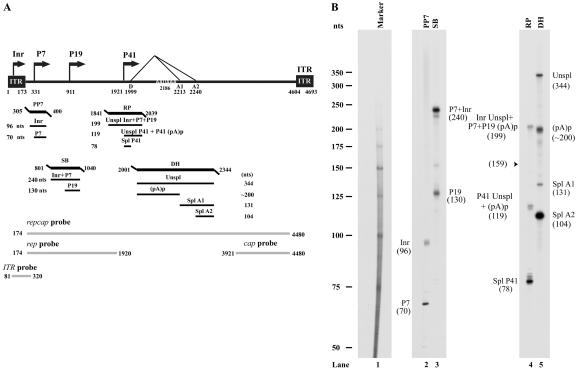
FIG. 2.
RPA analysis of B-AAV RNA generated from B-AAV-infected MDBK cells. (A) Schematic diagram of the B-AAV genome and the probes used for RPAs and Northern blots. The landmarks of transcription—the promoters (within the ITR [Inr], P7, P9, and P41), the splice donor site (D), the acceptor sites (A1 and A2), and the internal polyadenylation signal (pA)p—are shown. The RPA probes PP7 (nt 305 to 400), SB (nt 801 to 140), RP (nt 1841 to 2039), and DH (nt 2001 to 2344) are shown, along with the bands they are expected to protect and their predicted sizes. The probes repcap (nt 174 to 4480), rep (nt 174 to 1920), cap (nt 3921 to 4480), and ITR (nt 81 to 320), which are used for the Northern blot analysis in Fig. 3, are also shown. (B) Mapping of the B-AAV transcription units by RPA. A total of 10 μg of total RNA isolated 36 to 40 h after infection was protected by PP7, SB, RP, and DH probes, in individual reactions as indicated. Lane 1, 32P-labeled RNA markers (39), with sizes indicated to the left. The origins of the protected bands in lanes 2 and 5 are indicated. Spl, spliced RNAs; Unspl, unspliced RNAs; (pA)p, RNAs polyadenylated at the (pA)p site; Inr, RNAs generated from the initiator within the left ITR.