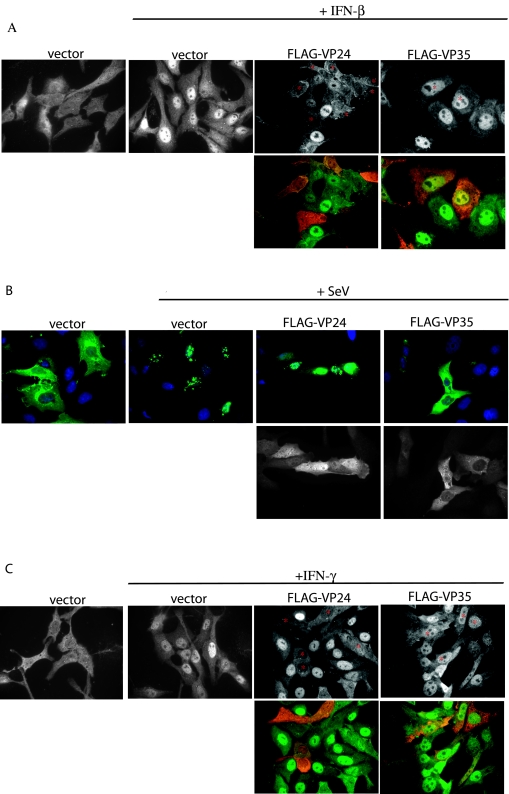
FIG. 3.
EBOV protein VP24 prevents IFN-mediated nuclear translocation of STAT1. (A) IFN-β treatment (30 min) of Vero cells causes STAT1 to relocate from the cytoplasm (vector) to the nucleus (vector + IFN-β). In cells expressing FLAG-VP24 (FLAG-VP24 + IFN-β; relevant cells marked with an asterisk), STAT1 fails to relocate to the nucleus after IFN-β treatment. IFN-β treatment of FLAG-VP35-expressing cells (FLAG-VP35 + IFN-β; relevant cells marked with an asterisk) causes STAT1 to relocate to the nucleus. Upper panels show only STAT1 images. Lower panels show the STAT1 images (green) merged with images of FLAG-tagged Ebola virus proteins (red). (B) Vero cells express GFP-IRF-3 in the cytoplasm in the absence of viral infection (vector), but translocate GFP-IRF-3 to the nucleus when infected with Sendai virus (vector + SeV). Coexpression of FLAG-VP35 prevents translocation of GFP-IRF-3 (FLAG-VP35 + SeV), but FLAG-VP24-expressing cells are still able to traffic GFP-IRF-3 to the nucleus (FLAG-VP24 + SeV). Upper panels show the GFP-IRF-3 (green) merged with Hoechst nuclear staining (blue). Lower panels show the FLAG-tagged Ebola virus proteins. (C) In Vero cells cotransfected with empty vector, STAT1 is predominately cytoplasmic in the absence of IFN-γ treatment (vector), but STAT1 concentrates in the nucleus after a 30-min treatment with IFN-γ (vector + IFN-γ). In the presence of FLAG-VP24, IFN-γ treatment fails to relocate STAT1 to the nucleus (FLAG-VP24 + IFN-γ).