Fig. 6. Characterization of the rGPx-1 by mass spectrometry.
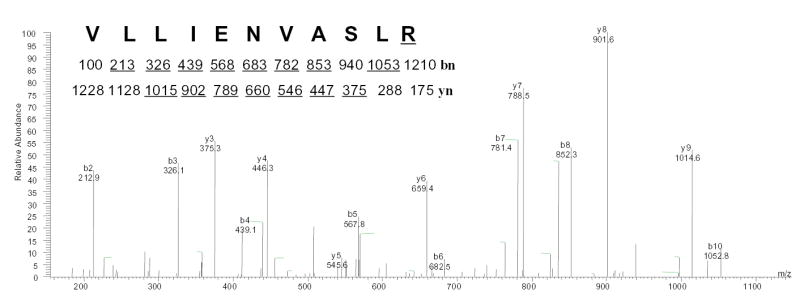
rGPx-1 purified from G418 treated COS7 cells was subjected to mass spectrometry analysis to determine the mass of the peptide, followed by amino acid sequencing by tandem mass spectrometry. The experimentally determined mass for the peptide, [M+2H]2+ =614.01, matched the predicted mass for the Sec-containing peptide (74–89) of rGPx-1 after conversion of the selenocysteine (residue 84) to arginine (underlined). This double-charged precursor ion was completely fragmented and was not detectable. yn and bn are the ions in which amino acid residues are sequentially cleaved from the NH2- terminal and COOH-terminal, respectively. The predicted molecular masses for fragment ions of types b and y are show under the sequence, and ions observed in the spectrum are underlined
