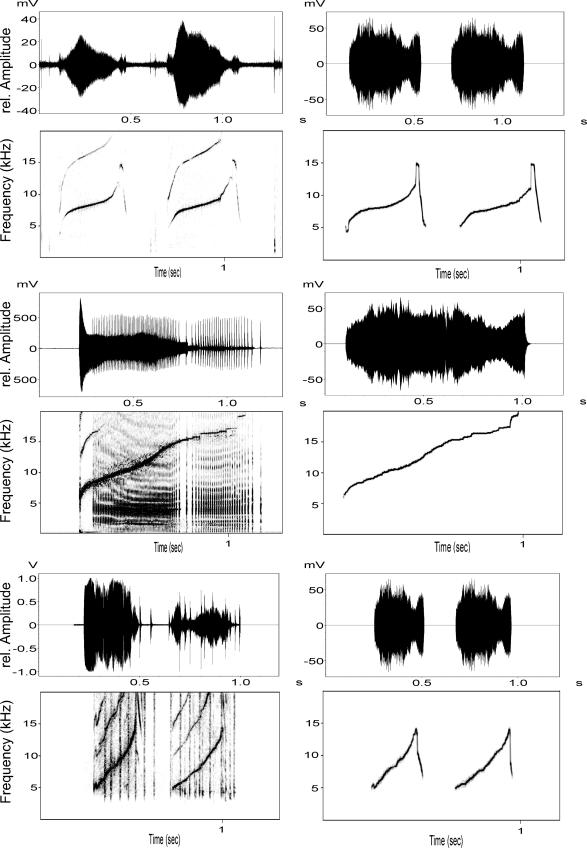
Fig. 1.
Spectrograms and waveforms of original whistles (Left) and their synthetic versions (Right) for three individuals. The first whistle is from a target animal, the second is its kin stimulus, and the third one is its nonkin stimulus whistle. This animal reacted more to its kin stimulus despite its own whistle being more similar to the nonkin stimulus. Synthetic whistles in this figure represent the input to the speaker system.