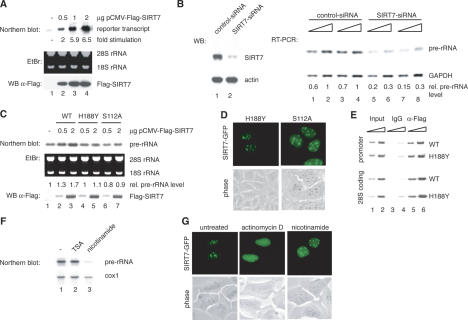
Figure 3.
SIRT7 is an activator of Pol I transcription. (A) Overexpression of SIRT7 stimulates Pol I transcription from an rDNA minigene reporter. 293T cells were cotransfected with a Pol I reporter plasmid and increasing amounts of an expression plasmid encoding Flag-SIRT7. RNA was isolated from transfected cells. The amount of reporter transcripts was determined by Northern blot analysis and quantified using a PhosphorImager. (Bottom panel) Western blot of the transfected cells probed with α-Flag antibody. (B) Knockdown of SIRT7 by RNAi impairs rRNA synthesis. (Left panel) Western blot of extracts from U2OS cells transfected with control-dsRNA (lane 1) or SIRT7-specific dsRNA (lane 2). (Right panel) Pol I transcription was analyzed by RT–PCR. RNA was isolated from cells treated with the respective dsRNAs. Increasing amounts of cDNA were used for PCR with primers that amplify a region of the 5′ external transcribed spacer of the human pre-rRNA. Results from two independent experiments are shown (one in lanes 1,2,5,6 and the other in lanes 3,4,7,8). As a control, RT–PCR was performed to analyze expression of GAPDH. The PCR-products were quantified using a PhosphorImager. (C) Overexpression of SIRT7H188Y and SIRT7S112A does not augment cellular Pol I transcription. (Top panel) Northern blot analysis of pre-rRNA transcripts from 293T cells transfected with different amounts of plasmids expressing wild-type SIRT7 or the point mutants H188Y and S112A. Pre-rRNA levels were determined by PhosphorImager. (Bottom panel) Expression levels of Flag-SIRT7, Flag-SIRT7H188Y, and Flag-SIRT7S112A were monitored on Western blots using α-Flag antibodies. (D) The SIRT7 mutants H188Y and S112A were expressed as GFP-tagged proteins in U2OS cells and their cellular localization was examined in live cells. (E) SIRT7H188Y is associated with rDNA. Flag-SIRT7 wild type (WT) and Flag-SIRT7H188Y mutant (H188Y) were overexpressed in 293T cells and assayed for binding to rDNA by ChIP. Immunoprecipitations were performed with mouse IgGs (lanes 3,4) and α-Flag (M2) antibodies (lanes 5,6); 0.5 and 1.5 μL of whole-cell extract DNA (lanes 1,2) and precipitated DNA (lanes 3–6) were amplified with rDNA primers A (promoter, top panel) and C (28S coding region, bottom panel). (F) Nicotinamide represses rRNA synthesis. NIH3T3 cells were cultured for 6 h in medium containing 40 nM TSA or 5 mM nicotinamide, and pre-rRNA levels were measured by Northern blot analysis using a 32P-labeled riboprobe specific for the 5′-transcribed external spacer. The blot was subsequently reprobed for cytochrome c oxidase (cox 1) mRNA. (G) Treatment with actinomycin D, but not with nicotinamide, releases SIRT7-GFP from nucleoli. U2OS cells expressing SIRT7-GFP were cultured in the presence of either 50 ng/mL of actinomycin D for 2 h to inhibit Pol I activity or 5 mM nicotinamide for 6 h to inhibit NAD+-dependent deacetylase activity. Localization of SIRT7-GFP was examined in live cells.