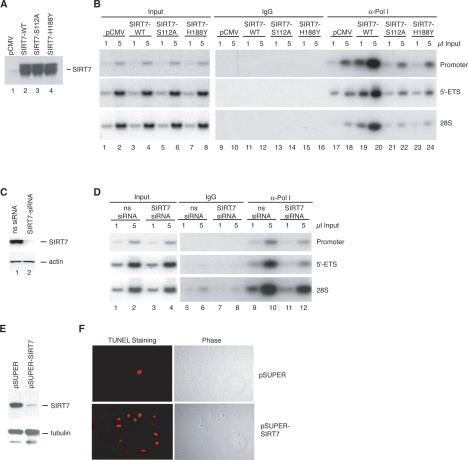
Figure 4.
SIRT7 stimulates the association of RNA Pol I with the rDNA. (A) Western blot showing overexpression levels of SIRT7 proteins. (B) Enrichment of Pol I at the transcribed region of the rDNA genes in the presence of ectopic SIRT7. Chromatin was prepared from cells harboring empty vector (pCMV) or plasmids expressing wild-type SIRT7 (SIRT7-WT) and mutant SIRT7 (SIRT7-S112A and SIRT7-H188Y). The chromatin was precipitated with α-RPA116 antibodies and analyzed by PCR with the primer pairs indicated on the right side of the figure. (C) Following siRNA transfections, whole-cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblot for SIRT7 and β-actin. (D) ChIP analysis of Pol I levels in cells transfected with siRNAs. Chromatin was prepared from cells transfected with nonspecific (ns) or α-SIRT7 siRNAs. The chromatin was precipitated with α-RPA116 antibodies and analyzed by PCR with the primer pairs indicated on the right side of the figure. (E) Western blot of SIRT7 and α-tubulin in 20 μg of whole-cell lysates from U2OS cells transfected with the pSUPER or pSUPER–shSIRT7 vectors. (F, right) U2OS cells transfected with the indicated vectors were fixed 5 d post-transfection and visualized by phase contrast. (Left) Apoptotic cells were detected by TUNEL staining.