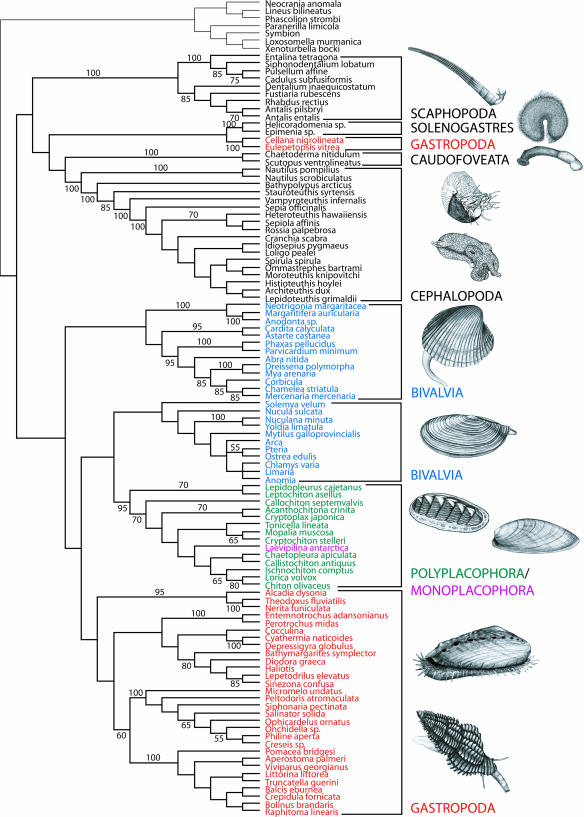
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic tree depicting the relationships of Monoplacophora to other molluscs based on the combined analysis of all molecular loci. Shown is strict consensus of two most parsimonious trees at 64,679 weighted steps (gap opening cost of 3, gap extension cost of 1, all base transformations cost 2) for the analysis of all data under direct optimization with tree fusing. Numbers on branches indicate jackknife support values. Gastropods (in red) and bivalves (in blue) appear diphyletic. Polyplacophora and Monoplacophora form a well supported clade (95% jackknife support). The monoplacophoran species (purple) appears nested within chitons (dark green), but nodal support for its exact position is low. The tree shows monophyly of molluscs, as well as that of Scaphopoda, Cephalopoda, Caudofoveata, and Solenogastres.