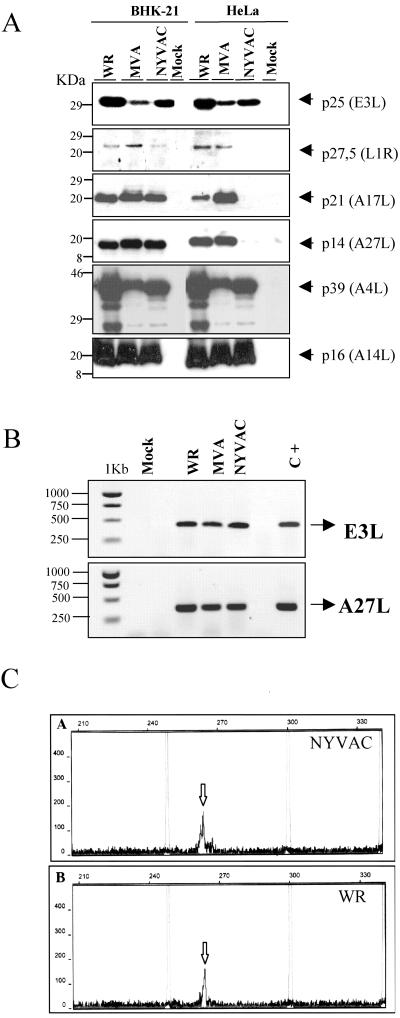
FIG. 4.
Expression of specific viral proteins under permissive and nonpermissive conditions. (A) Monolayers of BHK-21 and HeLa cells were mock infected (M) or infected at 5 PFU/cell with WR, MVA, or NYVAC, and cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting. Cell lysates were harvested at 24 h p.i., and equal amounts of proteins were fractionated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose paper, and reacted with different antibodies recognizing specific viral early proteins, such as p25, and viral late proteins, such as p27.5, p21, p14, p39, or p16. (B) Transcription of early and late viral genes. The transcription of E3L and A27L genes was determined by RT-PCR from total RNAs as described in Materials and Methods. Total RNA from uninfected cells and DNA extracted from MVA-infected cells were used as the negative (Mock) and positive (C+) control, respectively. (C) Primer extension product obtained using 2 μg of total RNA isolated from HeLa cells either uninfected (Mock) or infected at 5 PFU/cell with WR or NYVAC for 16 h. The sizes of the peaks from the GeneScan-500 ROX internal lane standards are shown (in base pairs). The arrows indicate the primer extension products (VIC-labeled cDNA) for the A27L gene. Peak height is a measure of fluorescence intensity and indicates the strength of the VIC signal. The peak heights for each sample were 177 for NYVAC (A), 164 for WR (B), and 55 for mock infected (not shown).