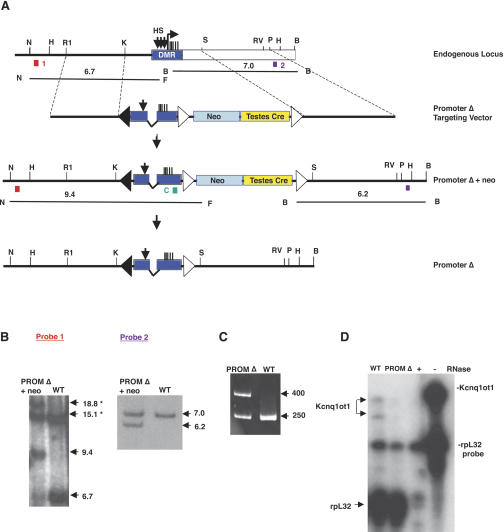
Figure 3.
Deletion of the Kcnq1ot1 promoter. (A) The endogenous locus is depicted as in Figure 1. The promoter Δ targeting vector contains a 244-bp deletion of the Kcnq1ot1 minimum promoter region and two DNase I hypersensitive sites, as well as the neomycin resistance gene (neo) and the Cre recombinase gene driven by a testes-specific promoter (testes-cre), flanked by loxP sites (open triangles). The loxP site at the 5′ end of the KvDMR (closed triangle) contains point mutations that reduce its recombination frequency with the downstream sites. The positions of the probes used in B (numbered colored boxes) and the fragments that are detected are indicated. (H) HindIII; (R1) EcoRI; (K) KpnI; (F) FspI; (P) PstI; (S) SspI; (RV) EcoRV; (B) BamHI; (N) NheI. (B) Southern blot analysis of DNAs prepared from wild-type (WT) and heterozygous PromΔ +neo mice after digestion with restriction enzymes and hybridization with the external probes as indicated in A. The asterisks denote the presence of additional bands that are the result of methylation of FspI sites. In wild-type cells, a 15.1-kb band derives from methylation of the maternal allele and the 6.7-kb band from the unmethylated paternal allele. In targeted ES cells, the targeted paternal allele produces both a new 9.4-kb band created by a FspI site in the neo gene and an additional 18.8-kb band when that site is methylated. (C) DNA from PromΔ (−neo) and wild-type (WT) mice was amplified by PCR using primers that span the neo and testes cre sequences that yield a 250-bp product derived from amplification of the nontargeted allele and a 400-bp product from the PromΔ (−neo) allele (Table 1). (D) RNA protection of placental RNA from wild-type (WT) and M. spretus × PromΔ mice (PromΔ) was performed using probe C located at the 3′ end of the DNA repeats in KvDMR and an rpL32 ribosomal protein RNA probe as a control. Radiolabeled probes were incubated in the presence (+) and absence (−) of RNase and yeast RNA.