Figure 2.
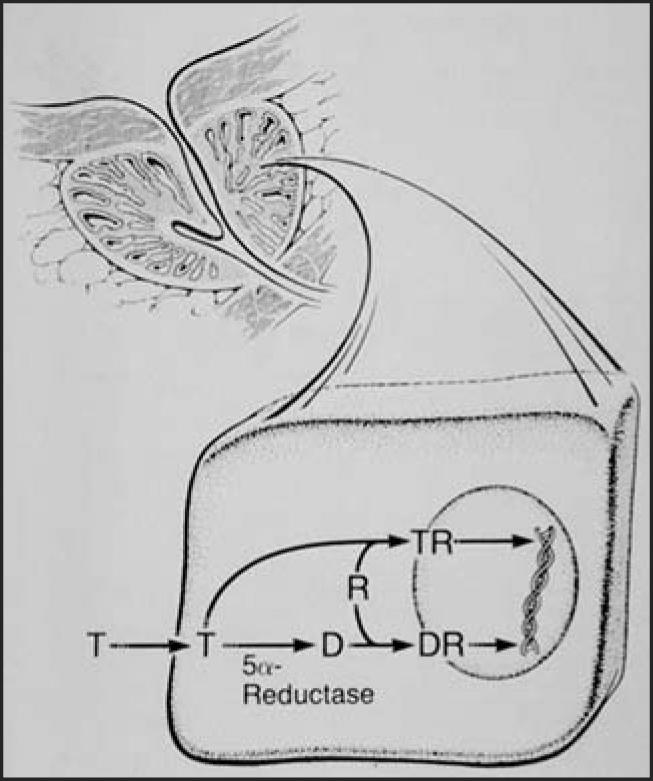
Within prostate cells, testosterone (T) is converted to dihydrotestosterone (D or DHT), which is the major intraprostatic androgen, binding preferentially to androgen receptors (R) to effect DNA synthesis. In the prostate, tissue DHT levels are some 10 times higher than T levels, just the opposite of serum levels.
