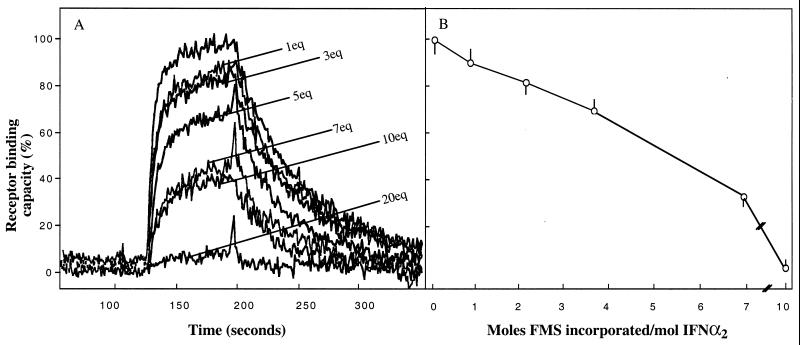
Figure 1.
Progressive modification of the amino acid moieties of IFN-α2 with FMS-OSu; loss of receptor binding capacity as a function of FMS moieties incorporated into IFN-α2. Human IFN-α2 was modified at pH 8.5 with increasing concentrations of FMS-OSu, ranging from 1 equivalent up to 20 molar equivalents of FMS-OSu. For each treatment, receptor binding capacity (A) and moles FMS introduced covalently into IFN-α2 (B) were determined. Receptor binding capacity toward immobilized ifnar2-EC was assessed by the reflectometric interference spectroscopy procedure. The rising and declining curves represent, respectively, ligand association and ligand dissociation from ifnar2-EC. Moles of FMS/moles of IFN-α2 were determined by UV absorption at 301 nm after dialysis and by mass spectroscopy (see Materials and Methods).