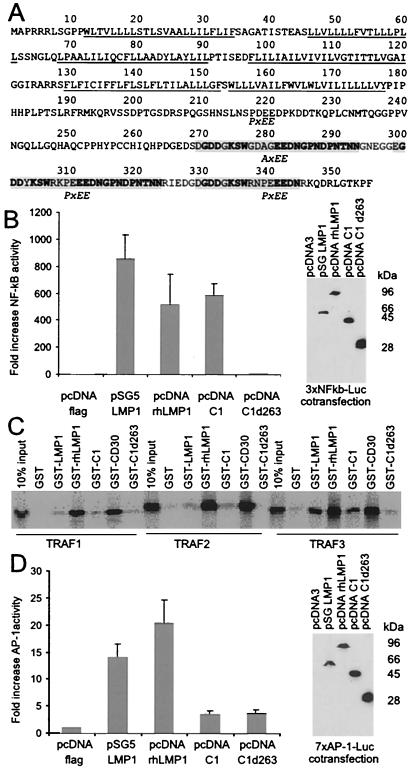
Figure 2.
CalHV-3 C1 amino acid sequence, activation of NF-κB, TRAF interaction, and lack of AP-1 induction. (A) The six hydrophobic transmembrane domains are underlined. Repeat elements in the carboxy terminus containing putative TRAF-binding sequence motifs (P/AxEE) are indicated by shading, with conserved residues shown in bold. (B) C1 induces NF-κB activity. A luciferase reporter gene under the control of three NF-κB-responsive elements (3xNFkB-Luc) was cotransfected into 293 cells with flag epitope-tagged expression vectors for EBV LMP1 (pSG5 LMP1), rhesus LCV LMP1 (pcDNA rhLMP1), CalHV-3 C1 (pcDNA C1), and a CalHV-3 C1 mutant truncated at aa 263 (pcDNA C1d263). Data were normalized for β-galactosidase expression and reported as fold induction versus transfection of 3xNFkB-Luc with the pcDNA-Flag as vector control DNA. Results represent the average of four independent transfections. Expression levels for LMP1 and C1 were confirmed after each transfection by Western blots probed with an anti-flag antibody (M2). A representative immunoblot is shown. (C) The C1 carboxy-terminal cytoplasmic domain can bind to TRAF proteins. GST fusion proteins with the complete (aa 179–355: GST-C1) or truncated (aa 179–263: GST-C1d263) C-terminal cytoplasmic domain of C1 were used to precipitate in vitro translated, 35S-labeled TRAF1, TRAF2, or TRAF3 proteins. TRAF binding to GST fusion proteins with EBV LMP1 (GST-LMP1), rhesus LCV LMP1 (GST-rhLMP1), and CD30 (GST-CD30) were included as positive controls. (D) C1 does not induce AP-1 activity. The same expression constructs as in B were cotransfected with a luciferase reporter gene under the control of seven AP-1-responsive elements (7xAP-1-Luc).