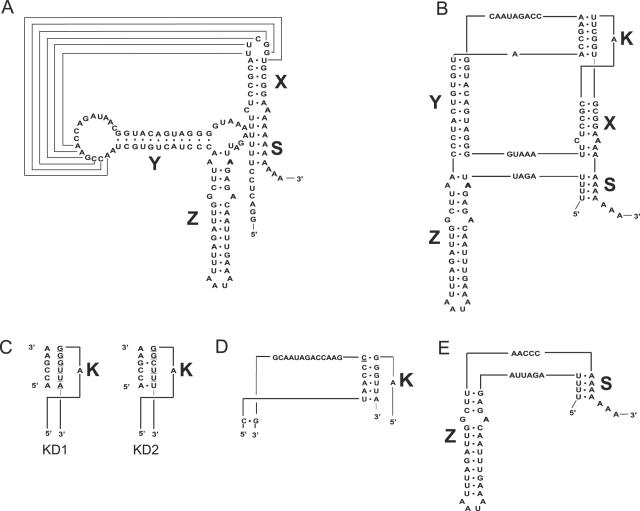
Figure 3.
Secondary and tertiary structures of wild type and mutant CVB3 3′NCRs. Secondary (A) and tertiary (B) structure of the wt CVB3 3′NCR. The 3′NCR consists of three hairpin domains, X, Y and Z. The structure can be closed by an interaction between the poly(A) with a 4 nt U-stretch overlapping the oriR and the 3D-coding region. The X domain can be stacked to the tertiary ‘kissing’ (K) interaction to form a coaxial helical element, which is connected by single-stranded nucleotide stretches to a second coaxial helical domain Z-Y. (C) Schematic representation of the kissing distortion mutants, KD1 and KD2, in which 6 and 4 bp, respectively, were mutated (underlined). (D) Partial 3′NCR sequence of a virus recovered after transfection with the KD1 mutant. The inserted cytosine residue in the recovered mutant is underlined. (E) The entire 3′NCR sequence of a virus recovered after transfection with the KD2 mutant.