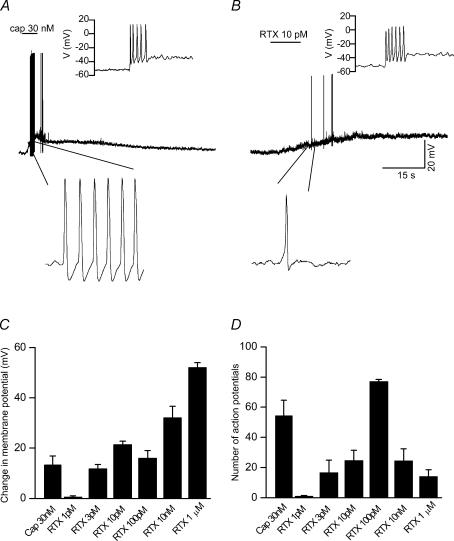
Figure 9. RTX- and capsaicin-induced membrane depolarization and the ability to generate action potentials.
A, capsaicin-induced (30 nm) membrane depolarization resulted in a burst of action potentials. Inset shows action potentials in response to current injection. B, RTX-induced (10 pm) membrane depolarization, which is slow and sustained and generated a few action potentials. Note that the membrane potential does not reach baseline even after washout. Inset shows action potentials in response to current injection. Representative regions are shown in expanded timescale below. C, summary graph showing the extent of membrane depolarization induced by capsaicin (30 nm) and different concentrations of RTX (1 pm−1 μm). D, summary graph showing the number of action potentials induced following application of capsaicin and RTX.