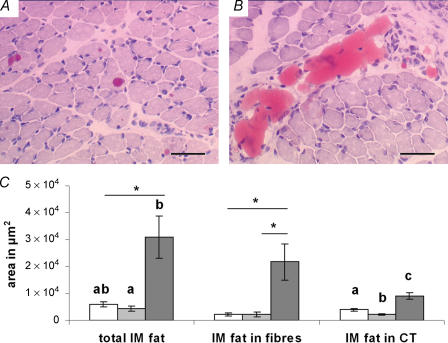
Figure 2. A maternal cafeteria diet promotes intramuscular fat accumulation in the offspring.
Histological analyses (oil red O) of intramuscular (i.m.) lipid accumulation in the semitendinosus muscles of 21-day-old rat pups born to mothers fed either chow ad libitum during gestation and lactation (C, □), the cafeteria diet during gestation followed by chow ad libitum during lactation (CDG, ░) or the cafeteria diet during gestation and lactation (CDW, ▒). A, lipids accumulated within muscle fibres (CDW group). B, lipids accumulated in the connective tissue (C group). C, quantified results from image analyses. Results are means ±s.e.m., n = 6 litters; different letters indicate statistically significant differences (P < 0.05); *0.05 ≤P≤ 0.10, by ANOVA followed by Games-Howell post hoc analysis. Scale bars are 50 μm.