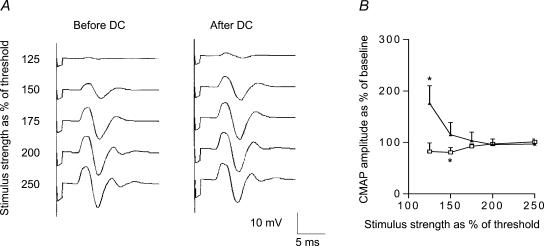
Figure 4. Effect of cathodal transcutaneous direct current (DC) stimulation and sham stimulation on the excitability of ulnar motor axons.
A, CMAP recordings from a representative subject showing the increase in CMAP amplitude just above the threshold in ulnar nerve after cathodal transcutaneous DC stimulation. B, Δ: cathodal polarization (n = 7 subjects); □: sham stimulation (n = 6); Y-axis: compound muscle action potential (CMAP) size expressed as a percentage of the control unconditioned response; X-axis: test stimulation strength expressed as percentage (%) of motor threshold; error bars: s.e.m. Note the increased excitability of low-threshold motor axons after cathodal DC offset. *P < 0.05 Wilcoxon signed rank test. Note the persistent increase in CMAP size after cathodal transcutaneous DC stimulation but not after sham stimulation.