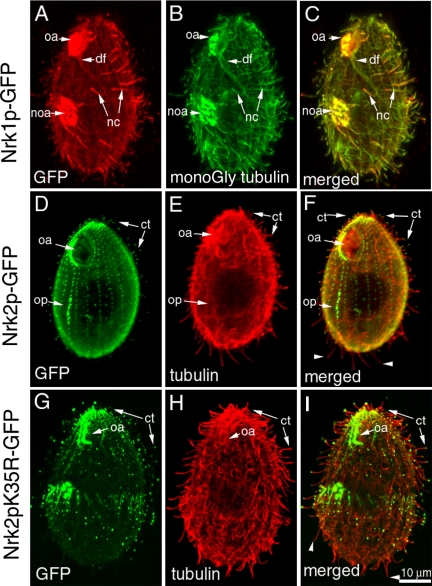
Figure 3.
Nrk1p and Nrk2p GFP fusion proteins preferentially localize to cilia and cortical microtubules. Immunofluorescent confocal images of cells overproducing Nrk1p-GFP (A–C), Nrk2p-GFP (D–F), and Nrk2p-K35R-GFP (G–I). Fluorescence of GFP is shown in A (red) and D and G (green). Top row, an Nrk1p-GFP–overproducing cell was processed for double immunofluorescence using anti-GFP antibodies (red in A) and TAP952 antibodies against monoglycylated tubulins (B). The TAP 952 antibody labels strongly new assembling cilia. Note that Nrk1p-GFP accumulates preferentially in TAP952-positive new cilia (C). Middle row, an Nrk2p-GFP–overproducing cell was subjected to double immunofluorescence with anti-GFP antibodies (D) and anti-total tubulin antibodies SG (E). Note an accumulation of Nrk2p-GFP at the tips of a subset of cilia located mainly in the ventral and anterior region of the cell (see F). Arrowheads indicate the absence of GFP label at tips of posterior cilia (F). Bottom row, an Nrk2p-K35R-GFP–overproducing cell labeled by anti-GFP antibodies (G) and total tubulin antibodies (H). The arrows point out a similar localization of Nrk2p-K35R-GFP at ciliary tips (ct) compared with Nrk2p. However, cilia of Nrk2p-K35R-GFP do not undergo shortening (I).