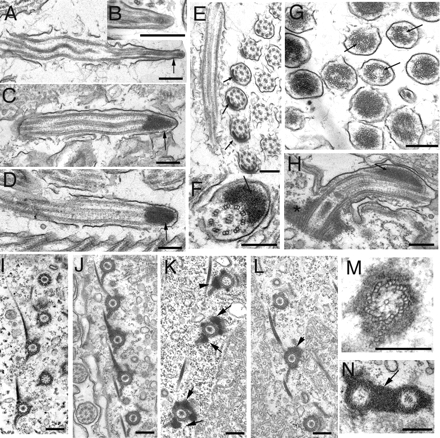
Figure 6.
Transmission electron microscopy of controls and cells overproducing NRKs. (A–D) Longitudinal sections of cilia of control cells with the Nrk2p-K35R-GFP transgene but without cadmium treatment (A) or wild-type cells treated with cadmium (B) or cadmium-treated Nrk2p-GFP–overproducing cells (C) and cadmium-treated Nrk2p-K35R-GFP–overproducing cells (D). (E) Cross-section of normal anterior adoral membranelle from NRK-2-dead kinase (without cadmium) showing normally occurring inclusions in these cilia. Note that inclusions are present but they are limited to only one row of cilia in the oral membranelle (F) Cross-sections of a locomotory cilium in the Nrk2p-K35R-GFP–overproducing cell. (G) Cross-section of a group of cilia at the level of ciliary tips in cells overproducing Nrk2p-GFP. Note displacements of axonemal microtubules (arrows). (H) Longitudinal section of a cilium from a Nrk2p-K35R-GFP–overproducing cell treated with cadmium. Note the lateral location of the electron-dense deposit (arrows). (I) Section of a control cell cortex treated with cadmium. (J–N) Images showing sections of the cortical regions of Nrk2p-GFP cells (J, K, M, and N) and Nrk2p-K35R-GFP cells (L) all treated with cadmium. Note electron-dense deposits around microtubules of basal bodies as well as associated microtubule bundles; these are asymmetrically localized in Nrk2p-GFP cells (K, arrows) and Nrk2p-K35R-GFP cells (L). Bar, 0.2 μm.