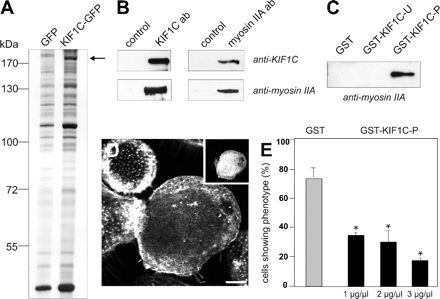
Figure 6.
KIF1C interacts with nonmuscle myosin IIA. (A) HUVEC lysates immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibody coupled to magnetic beads. Silver-stained PAA gel, left lane: cells transfected with pEGFP-N1 as control; right lane: cells transfected with KIF1C-GFP construct. Arrow indicates band subsequently identified by MALDI as nonmuscle myosin IIA. Molecular mass in kilodaltons is indicated on the left. (B) KIF1C and myosin IIA coprecipitate from macrophage lysates. Immunoprecipitation of macrophage lysates, using rabbit IgG as control, KIF1C-specific antibody or myosin IIA-specific antibody. Western blots developed with antibody indicated at the right. (C) GST-pull down of macrophage lysates. Western blot probed with anti-myosin IIA antibody. Denominations of GST-fused polypeptides used for pull down are given above each lane. (D) Microinjection of macrophages with GST-KIF1C-P disrupts podosomes. Laser scanning confocal micrograph of substrate-attached part of cell, specimen stained for F-actin and rat IgG (inset) as an injection marker. Bar, 10 μm. (E) Evaluation of podosome formation in macrophages microinjected with GST-KIF1C-P polypeptide. Values are given as mean percentage ± SD of total counts. For each value, 3 × 30 cells were evaluated. Cells with podosomes: GST control (0.5 μg/μl), 73.3 ± 7.7%; GST-KIF1C-P (1 μg/μl), 34.4 ± 1.5%; GST-KIF1C-P (2 μg/μl), 30.0 ± 7.3%; GST-KIF1C-P (3 μg/μl), 17.8 ± 1.5%. For differences between control values and values gained with KIF1C-P injections, a p value < 0.03 was considered significant (indicated by asterisk).